Figure 10.
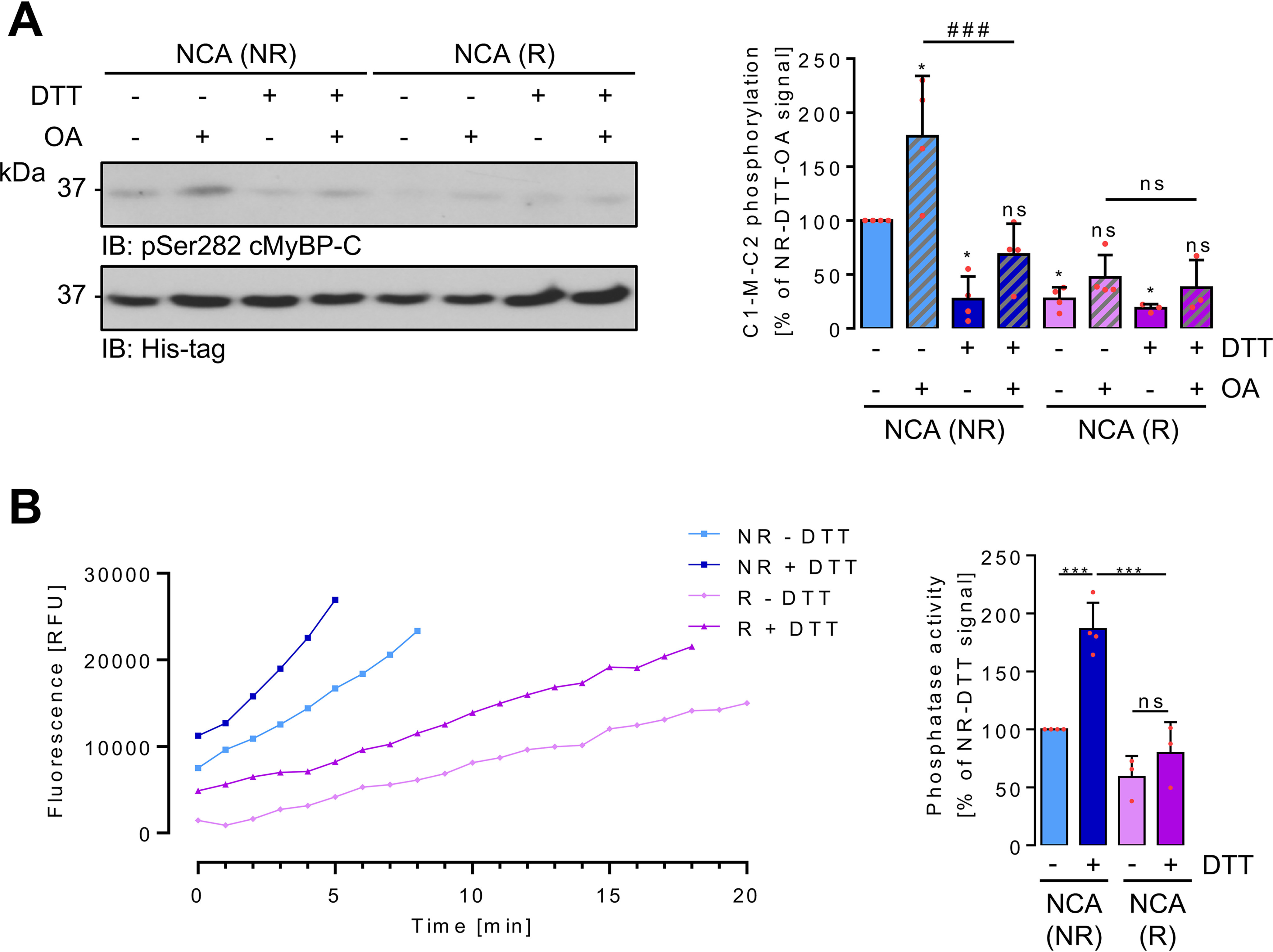
Oxidation-mediated effects on PKA and PP2A-C activity in myofilaments. A, Triton X-100–insoluble myofilament-containing fractions were prepared under NR or R conditions from ARVMs after exposure to NCA. Samples were split and in vitro phosphorylation of His6-tagged C1-M-C2 cMyBP-C at Ser-282 analyzed after addition of vehicle (DMSO), DTT to reduce oxidative modifications, or OA to inhibit PP1α and PP2A. Equal substrate protein content was demonstrated by immunoblotting with an anti-His antibody. The scatter plot summarizes results for C1-M-C2 phosphorylation from 3 to 4 independent experiments. Data are expressed as % of the signal of the NR signal without any additions. *, p < 0.05 for comparison with the NR nontreated sample; ####, p < 0.001 for comparison of the NR + OA sample in the presence or absence of DTT. Analysis by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test (interaction, F = 7.39, p = 0.0013; harvesting conditions, F = 36.99, p < 0.0001; IVK conditions, F = 14.22, p < 0.0001). B, Triton X-100–insoluble myofilament-containing fractions were prepared under NR or R conditions from ARVMs after exposure to NCA. Samples were split and phosphatase activity over time recorded after addition of vehicle (PBS) or DTT and DiFMUP (representative traces). The bar chart summarizes the results of 3 to 4 independent experiments expressed as % of the phosphatase activity measured under NR condition without any addition. ***, p < 0.001 for comparison with the NR DTT-treated sample. Analysis by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test (interaction, F = 10.14, p = 0.0097; harvesting conditions, F = 51,53, p < 0.0001; phosphatase assay conditions, F = 27,01, p < 0.0004). ns, nonsignificant.
