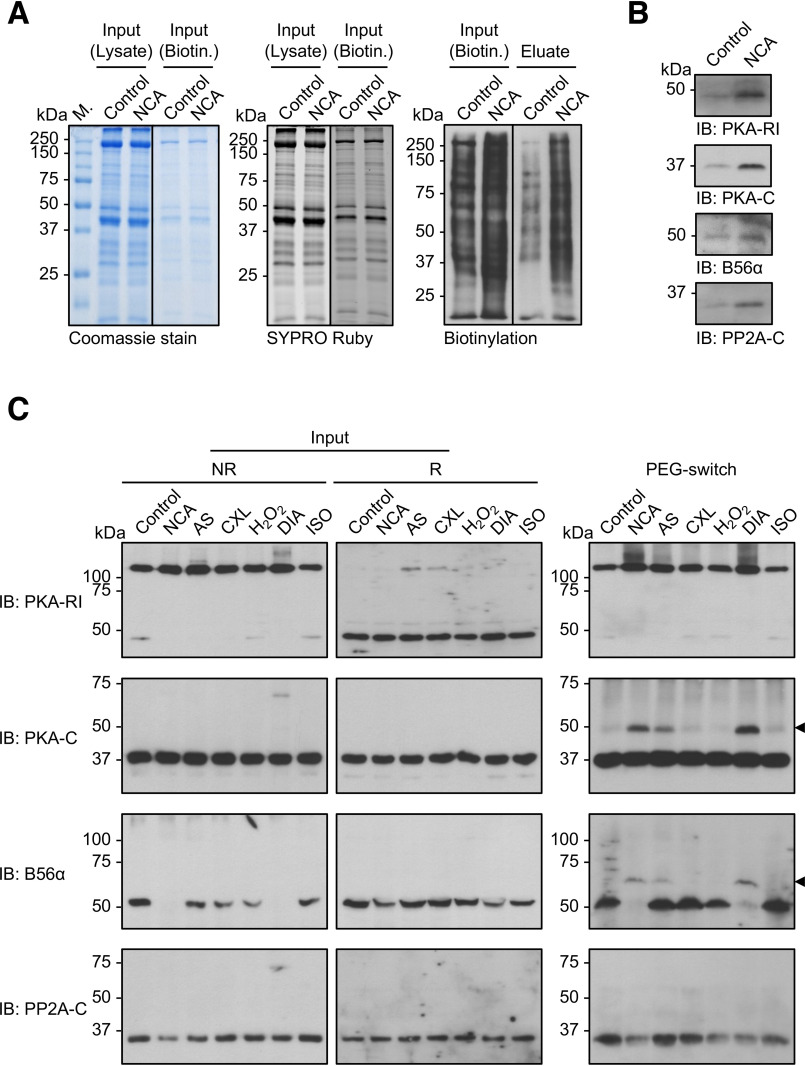
Figure 8.
Investigation of PKA and PP2A oxidation in intact ARVMs. A, biotin-switch analysis. Lysates from ARVMs exposed to vehicle (DMSO; 30 min) or NCA (100 µmol/liter; 30 min) were subjected to biotin labeling of oxidized thiol groups and subsequently biotinylated proteins were enriched by streptavidin pulldown. Total protein content before biotin labeling (Input; Lysate) or before streptavidin-pulldown (Input; Biotin) is demonstrated by Coomassie (left panel) or SYPRO Ruby staining (middle panel). Protein biotinylation levels correlated with protein oxidation in samples before (Input; Biotin) and after streptavidin-pulldown (eluate) was visualized by chemiluminescent detection with streptavidin-HRP (right panel). Blots are representative of three independent experiments. B, PKA-RI, PKA-C, B56α, and PP2A-C were detected in the streptavidin-pulldown samples by Western immunoblot analysis (IB). C, PEG-switch analysis. Lysates from ARVMs exposed to vehicle (control), NCA (100 µmol/liter, 30 min), AS (300 µmol/liter, 15 min), CXL-1020 (300 µmol/liter, 15 min), H2O2 (100 µmol/liter, 10 min), DIA (500 µmol/liter, 10 min), or ISO (10 nmol/liter, 10 min) were analyzed by nonreducing (left panel) or reducing (middle panel) Western immunoblot analysis for PKA-RI, PKA-C, B56α, and PP2A-C. Lysates were subjected to PEG tag labeling of oxidized thiol groups and subsequent detection of oxidized proteins via a mass shift was performed by western immunoblotting for PKA-RI, PKA-C, B56α, and PP2A-C (right panel). Blots are representative of three independent experiments.