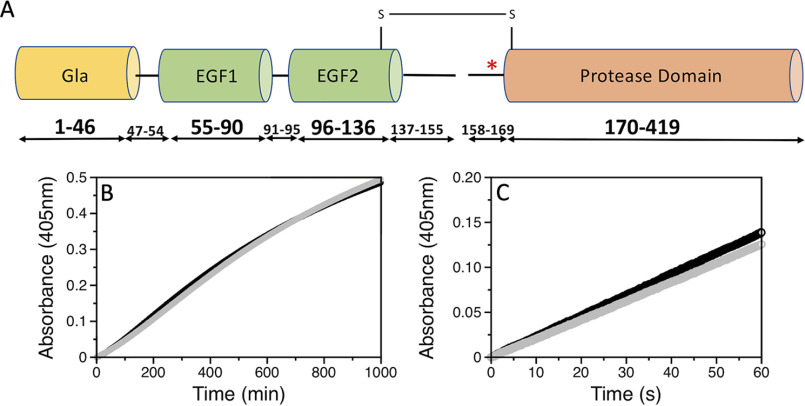
Figure 1.
A, schematic representation of protein C comprising the Gla (residues 1-46), EGF1 (residues 55-90), EGF2 (residues 96-136), and protease domains (residues 170-419). Three linkers connect the different domains. A dipeptide consisting of residues Lys156 and Arg157 is removed from the third linker to produce a two-chain zymogen where the light chain (residues 1-155) and heavy chain (residues 158-419) remain connected through the Cys141–Cys277 disulfide bond. Cleavage by thrombin at Arg169 removes the activation peptide (red asterisk, residues 158-169) and produces APC. B, thrombin-catalyzed activation of the AF555/AF647 labeled (black) and unlabeled (gray) protein C S12C/R312C mutant. Activation was monitored by a progress curve using the APC-specific substrate H-D-Asp-Arg-Arg-p-nitroanilide at 405 nm under experimental conditions: 20 mm Tris, 145 mm NaCl, 5 mm EDTA, 0.1% PEG8000, pH 7.5, at 37 °C. C, hydrolysis of the chromogenic substrate S-2366 by the AF555/AF647-labeled (black) and unlabeled (gray) APC S12C/R312C mutant monitored at 405 nm under experimental conditions: 20 mm Tris, 145 mm NaCl, 5 mm CaCl2, 0.1% PEG 8000, pH 7.5, at 25 °C. Saturating amounts of the inhibitor hirudin (250 nm) were added to rule out contamination by thrombin activity.