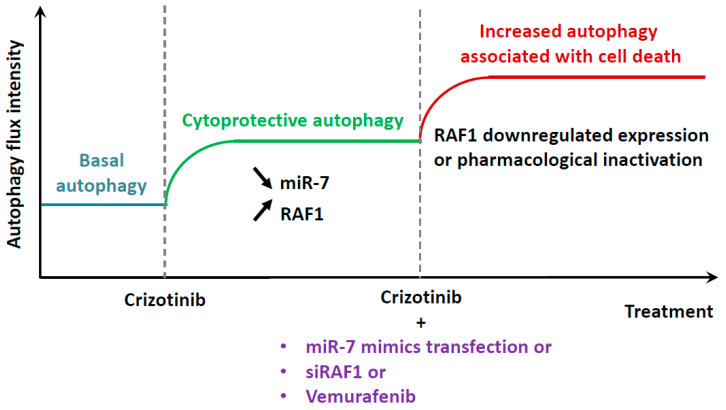
Figure 7.
The proposed model of action of NPM-ALK and RAF1 inhibitions on autophagy flux and cells outcome. The pharmacological inactivation of the NPM-ALK oncogene in NPM-ALK+ ALCL was previously shown to induce a cytoprotective autophagic flux. This status was shown to be associated with the downregulation of miR-7-5p levels and the increased expression of one of its targets: RAF1. When pharmacological or molecular tools allowing RAF1 inactivation were used in combination with NPM-ALK inhibition, the autophagy flux was potentiated and associated with increased cell death, therefore, highlighting the superiority of the co-treatment to kill NPM-ALK+ lymphoma cells.