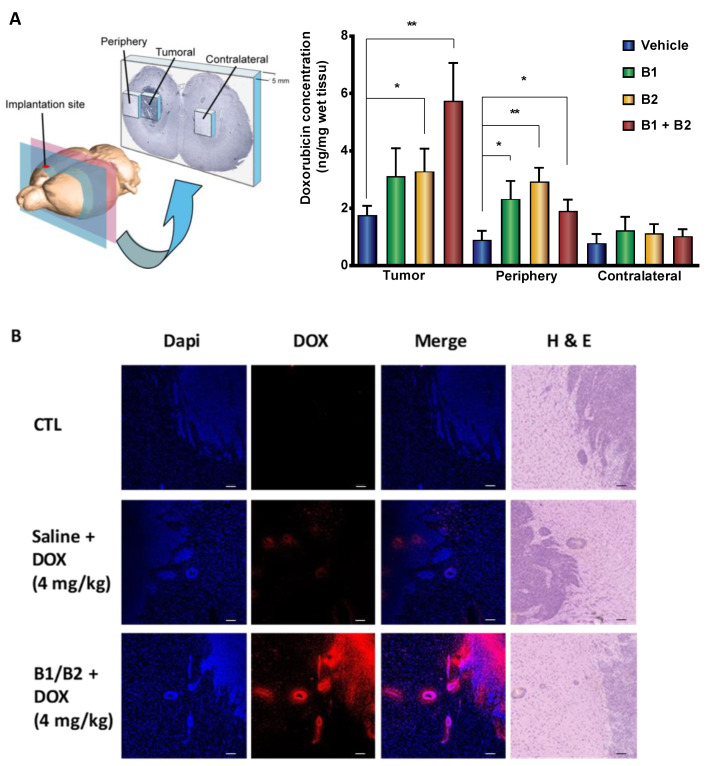
Figure 1.
Intracarotid administration of synthetic kinin B1 and/or B2 receptor agonists selectively enhances doxorubicin (DOX) delivery to tumors in F98 glioma-bearing rats. (A) Histographic representation with 3D schematic drawing of dissection of rat brain (left panel) and spectrofluorometric quantification of DOX (Ex/Em: 480/590 nm) in sized-related samples from tumoral, peritumoral, and matched tissues from the contralateral hemisphere (right panel). Data are reported as means ± SEM for n = 7–9 animals per group. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 vs. vehicle-treated group, Student’s unpaired t-test (GraphPad Prism 8.2). (B) Imaging of DOX distribution in rat tumor/peritumoral sites by confocal microscopy. Representative confocal midsection images of brain tumor sections of F98 glioma-bearing rats left untreated or treated with DOX solely or combined with B1 receptor (B1R) and B2R agonists (n = 2 rats/group; qualitative data). Contiguous sections stained with Dapi (to identify cell nuclei) and H and E are shown. Scale bar = 150 µm.