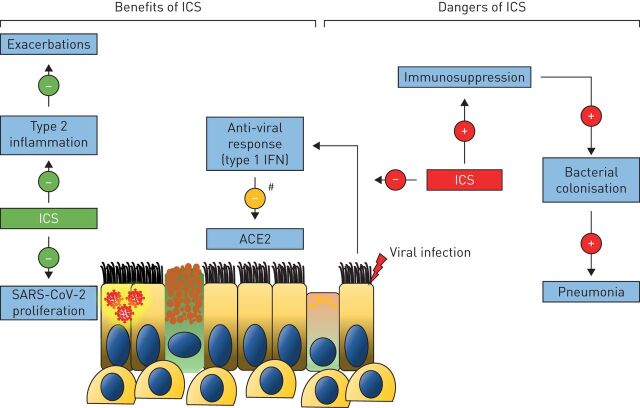
FIGURE 2.
Inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) use in COPD: implications for coronavirus disease 2019. ICS prevent exacerbations in eosinophilic COPD patients, probably in part by targeting type 2 inflammation in these individuals. ICS may have further benefit by reducing the ability of severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) to proliferate, and by limiting SARS-CoV-2 cellular entry by reducing angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE)2 expression as a result of inhibiting type 1 interferon (IFN) production. However, immunosuppression may increase susceptibility to respiratory infections leading to secondary bacterial colonisation and increasing the risk for pneumonia in some individuals. #: ICS reduces ACE2 expression by reducing type 1 IFN production.