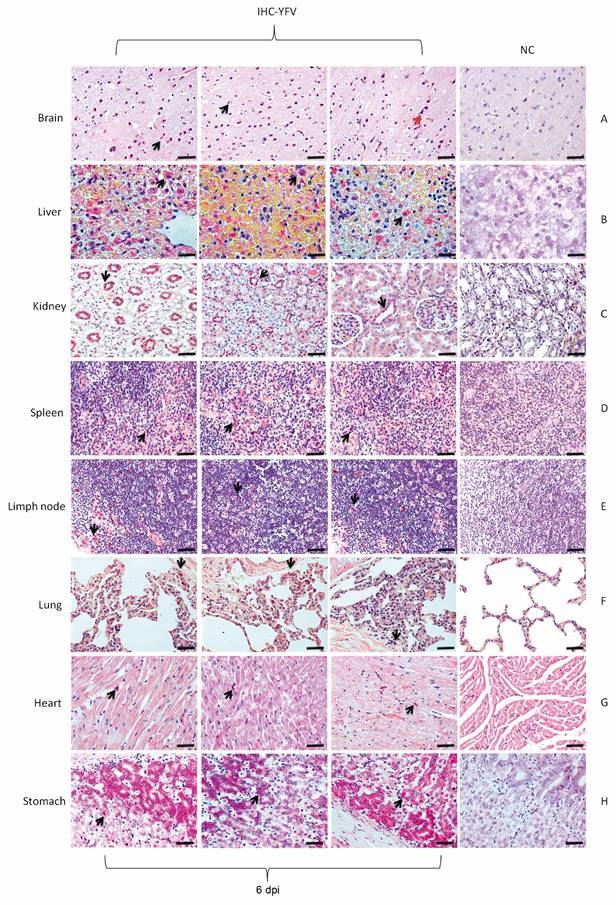
Fig. 4: detection of viral antigens in the organs of the squirrel monkeys (Saimiri spp.) infected with yellow fever virus (YFV) that died at 6 days post-infection (dpi). (A) In the brain, immunostaining was predominant in glial cells in the neural parenchyma (black arrow) and neurons (red arrow). (B) YFV tropism by infecting hepatocytes (black arrow) was obvious at 6 dpi. (C) In the kidney, the immunostaining was marked in the renal tubules (black arrow). (D, F) In the spleen, lymph node and lung, immunostaining was enhanced in the mononuclear cells. (G, H) Myocardial and stomach cells were the preferred target of YFV at 6 dpi (black arrow). 400X (20 µm). IHC: immunohistochemistry; NC: negative control.