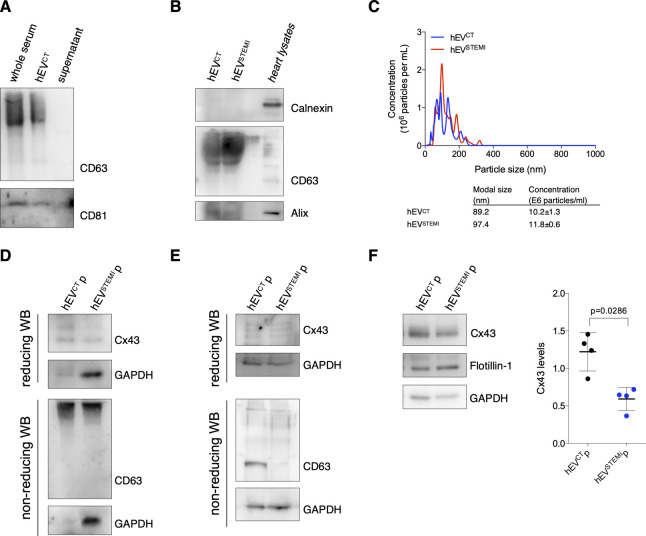
Figure S8. Cx43 levels decrease in extracellular vesicles (EVs) from human serum of STEMI patients.
(A) EVs were isolated from human serum using a polymer-based kit. Non-reducing WB was performed in whole serum, EV pellet, and supernatant, to verify the efficiency of the kit in precipitating CD63 and CD81-positive EVs. (B) Non-reducing WB of circulating EVs (30 μg total protein) derived from the serum of control (hEVCT) or STEMI patients (hEVSTEMI). CD63 and Alix were used as positive EV markers and Calnexin was used as a negative marker. Heart lysates were used as control. (C) Nanoparticle tracking analysis of circulating human EVs. Concentration indicates the number of particles per ml of serum sample. (D) EVs were isolated from the plasma of control (hEVCTp) or STEMI patients (hEVSTEMIp) using a polymer-based kit. WB analysis of Cx43 was performed in reducing conditions, whereas WB for CD63 was performed in non-reducing conditions. GAPDH was used as control. (E) EVs were isolated from the plasma of control (hEVCTp) or STEMI patients (hEVSTEMIp) by size-exclusion chromatography. WB analysis of Cx43 was performed in reducing conditions, whereas WB for CD63 was performed in non-reducing conditions. GAPDH was used as control. (F) WB analysis of EVs isolated from the plasma of control (hEVCTp) or STEMI patients (hEVSTEMIp), by differential ultracentrifugation. GAPDH and Flotillin-1 were used as controls (n = 4).