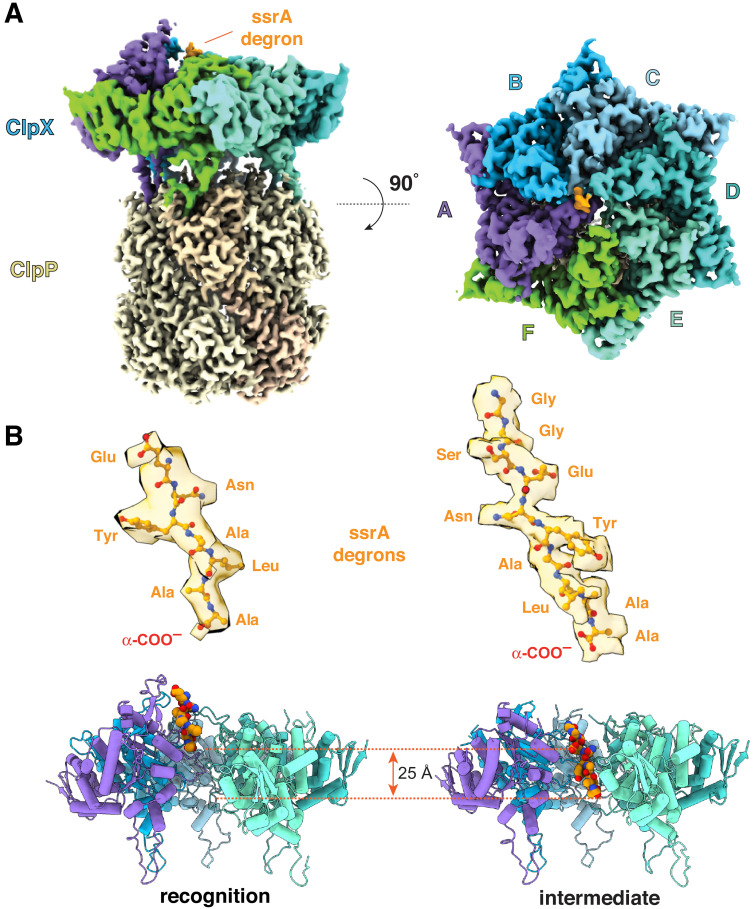
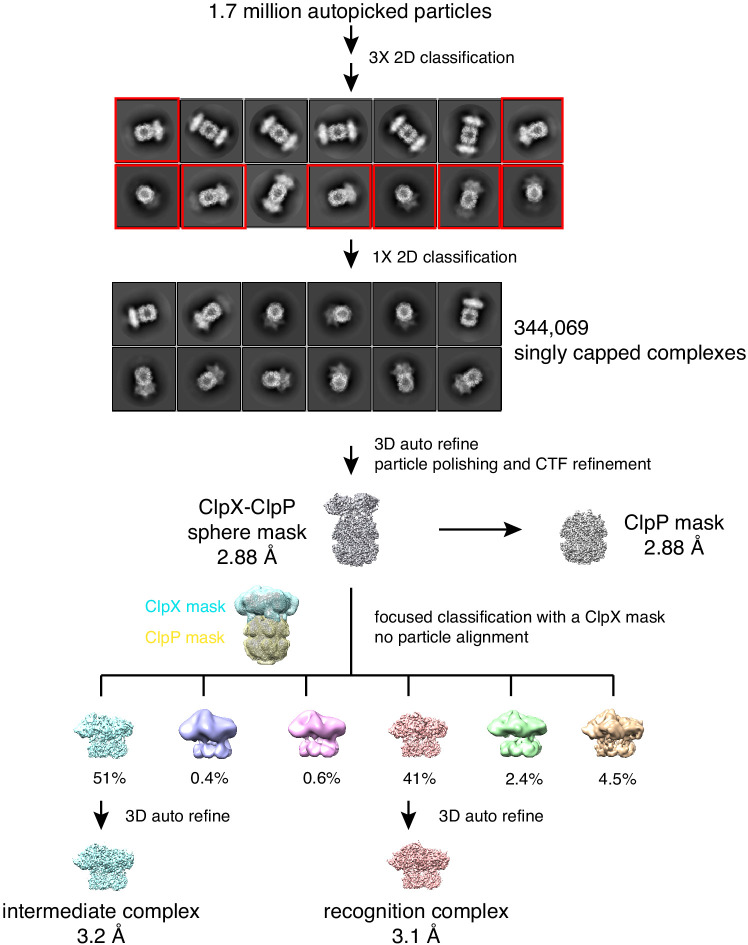
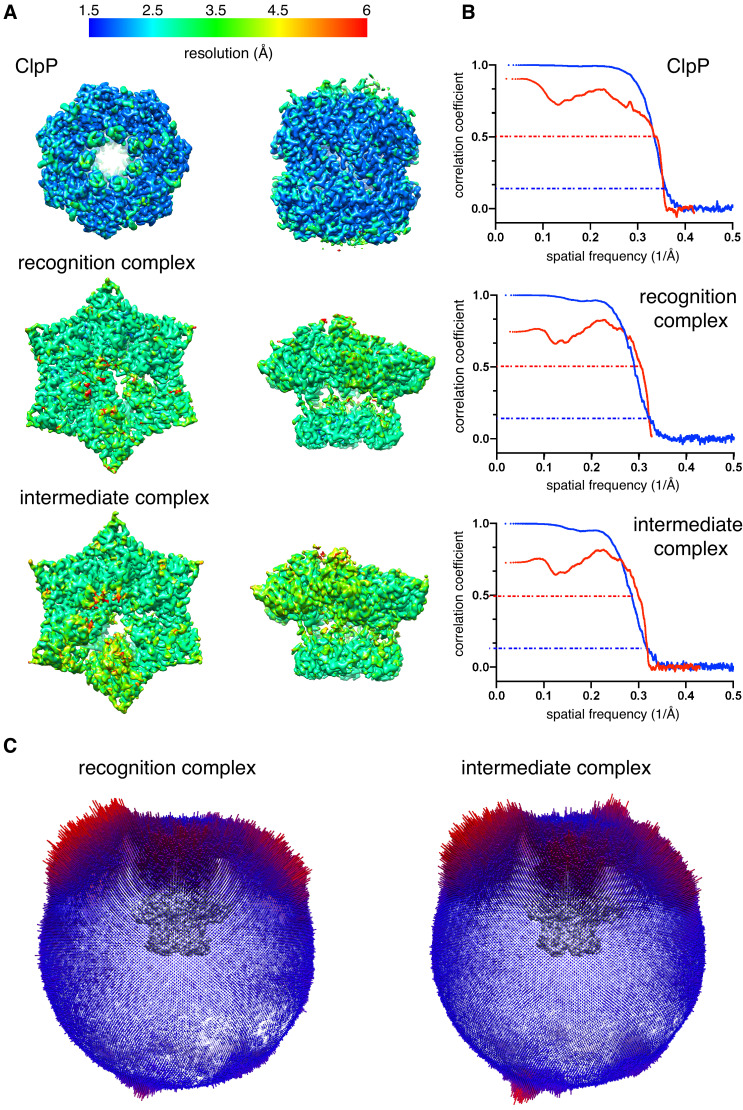
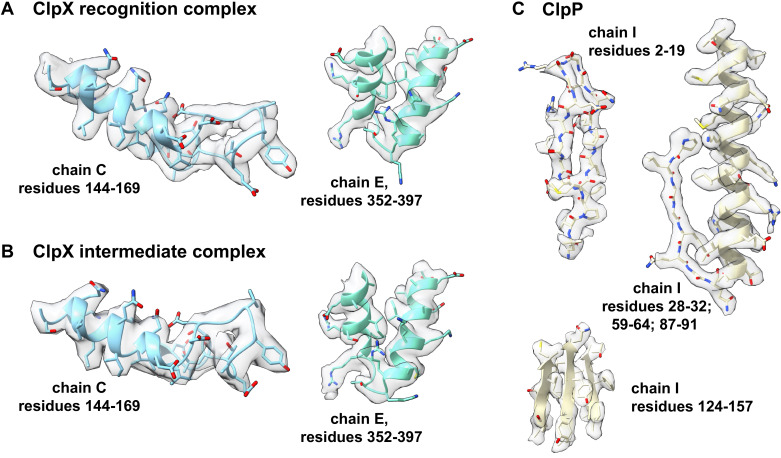
Figure 1. ClpXP complexes with ssrA degrons.
(A) Side and top views of the composite cryo-EM density from the recognition complex. (B) The upper portion of the panel shows transparent density for the ssrA degron (stick representation) in the recognition and intermediate complexes; the lower portion shows the offset positions of the ssrA degron (space-filling representation) in the channel of ClpX (cartoon representation) in both complexes after removal of subunit F. In this and all subsequent figures, ClpX is colored blue, green, or purple; ClpP is yellow; and substrate is orange/gold.