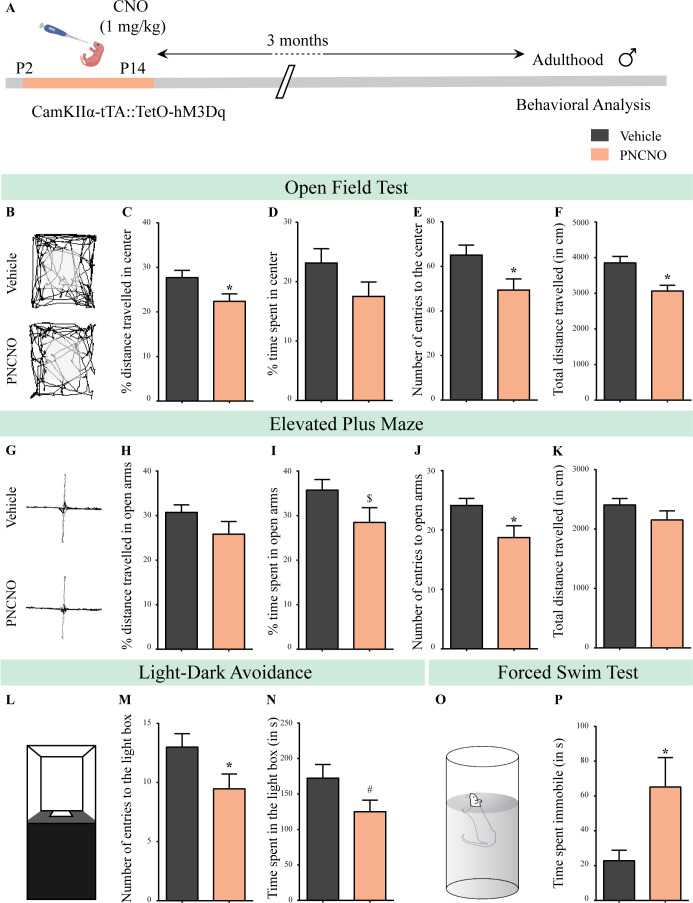
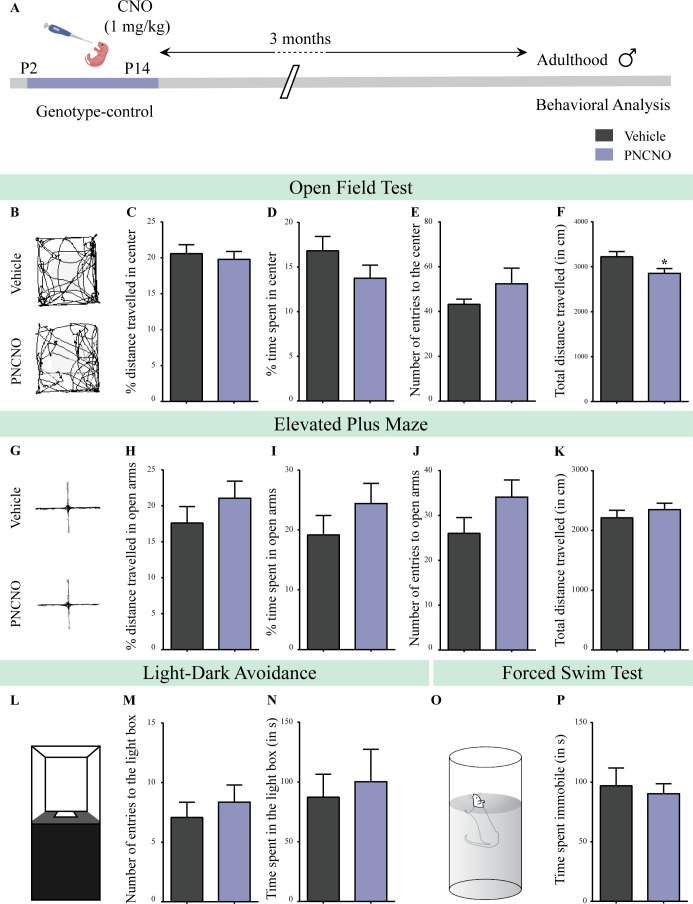
Figure 2. Chronic chemogenetic activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons during the early postnatal window results in a long-lasting increase in anxiety- and despair-like behavior in adult male mice.
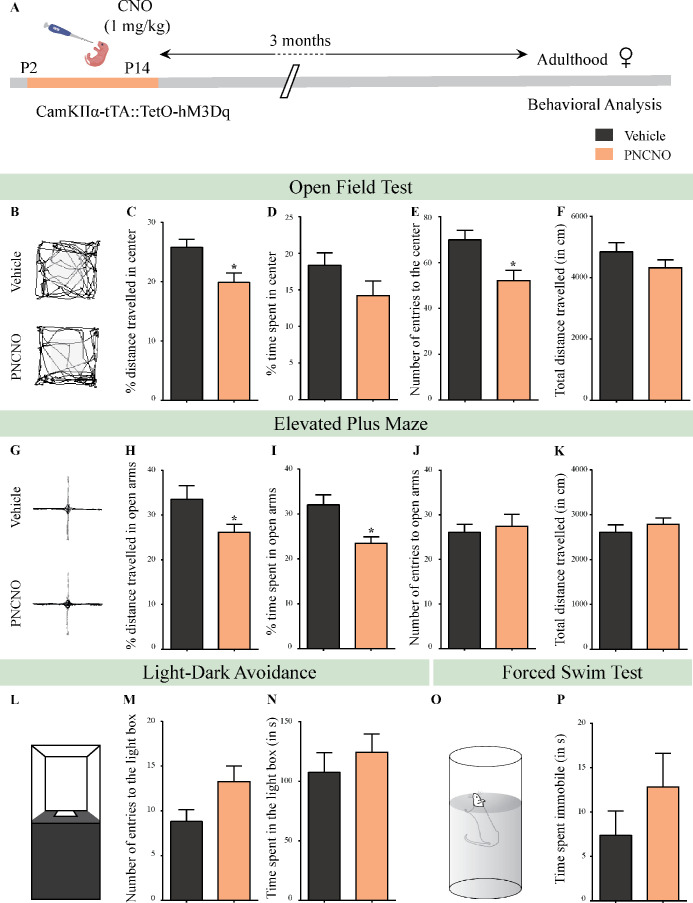
(A) Shown is a schematic of the experimental paradigm to induce chronic CNO-mediated hM3Dq DREADD activation in CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons using bigenic CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq mouse pups that were fed CNO (PNCNO; 1 mg/kg) or vehicle from P2 to P14 and then left undisturbed for 3 months prior to behavioral analysis performed in adulthood on male mice. (B) Shown are representative tracks of vehicle or PNCNO-treated CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq bigenic adult male mice in the open field test (OFT). A history of chronic postnatal hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons resulted in increased anxiety-like behavior on the OFT in adulthood, as noted by a significant decrease in the percent distance traveled in center (C), number of entries to the center (E), and the total distance traveled in the OFT arena (F) in PNCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 15 per group). The percent time spent in the center was not significantly altered (D) in PNCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls. (G) Shown are representative tracks of vehicle or PNCNO-treated CamKIIα-tTA::TetO-hM3Dq bigenic adult mice on the elevated plus maze (EPM). Adult mice with chronic postnatal hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons exhibited increased anxiety-like behavior on the EPM as revealed by a significant decrease in the number of entries to the open arms (J), and a trend toward a decrease in percent time spent in the open arms (I) in PNCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 15 per group). The percent distance traveled in the open arms (H) and the total distance traveled in the EPM arena (K) was not altered in PNCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls. (L) Shown is a schematic of the light-dark box used to assess anxiety-like behavior. Chronic postnatal hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons resulted in an increased anxiety-like behavior in the LD box test in adulthood, as revealed by a significant decline in the number of entries to the light box (M), and a trend toward decline in the time spent in the light box (N) in PNCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 15 per group). (O) Shown is a schematic representation of the forced swim test (FST) apparatus used to assess despair-like behavior. Chronic postnatal hM3Dq DREADD activation of CamKIIα-positive forebrain excitatory neurons resulted in an increased despair-like behavior on the FST in adulthood, as revealed by a significant increase in time spent immobile (P) in PNCNO-treated mice as compared to vehicle-treated controls (n = 13 per group). Results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. *p<0.05, $p=0.08, #p=0.07; as compared to vehicle-treated controls using the two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test.