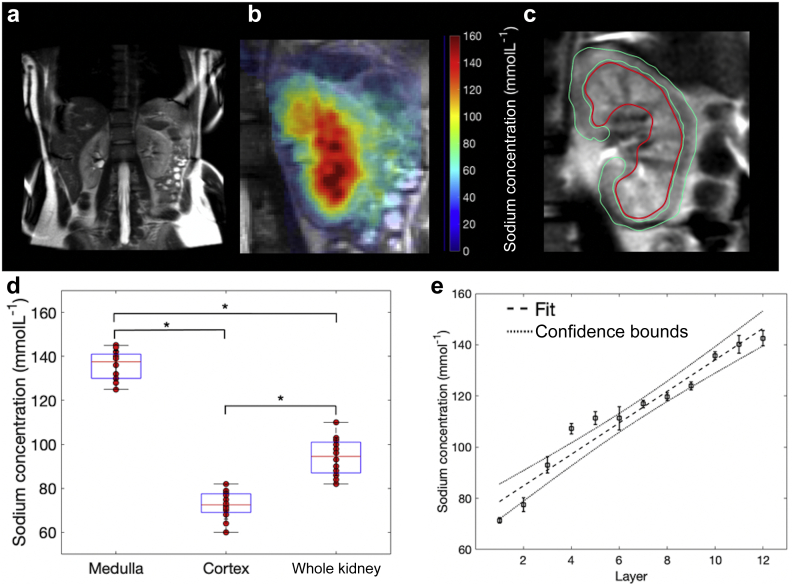
Figure 1.
Sodium imaging of the human kidney. (a) Coronal proton T2 magnetic resonance imaging from site A. (b) Fused sodium concentration maps and proton imaging from site A. (c) Regions of interest showing the cortex (green) and medulla (red). (d) Manual segmentation results from the sodium imaging revealing a significant difference between regions of interest. ∗Significant, P < 0.05. (e) Average corticomedullary sodium gradient from all volunteers across both sites, R2 = 0.94, P < 0.05.