Figure 2.
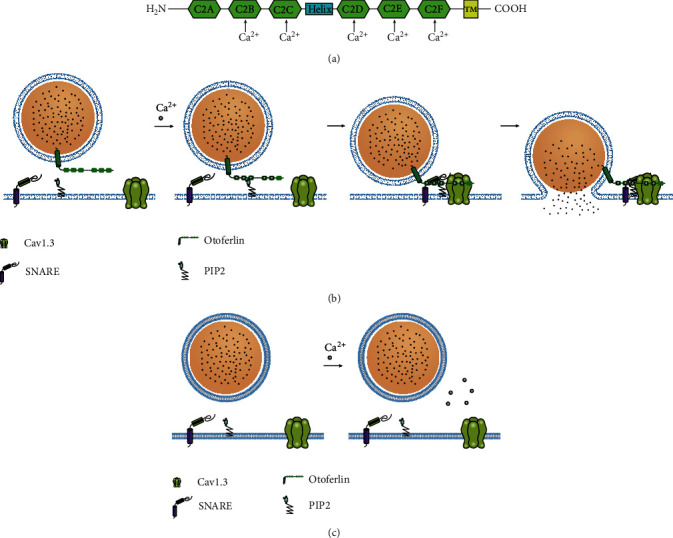
Schematic of the structure and function of Otoferlin. (a) Diagram of Otoferlin depicting the six C2 domains, labeled C2A–C2F, and the transmembrane domain (TMD). The binding of Ca2+ is indicated for all C2 domains with the exception of C2A. (b) The function of Otoferlin in vesicle fusion. (i) Ca2+-dependent phospholipid binding targets the presynaptic membrane via interaction with PIP2. (ii) Ca2+-dependent approximation of vesicular and plasma membranes. (iii) Interaction with proteins such as SNARE and the Cav1.3 channels to mediate Ca2+-triggered fusion. (c) Loss of Otoferlin. The extracellular transport of synaptic vesicles in the IHCs ceases completely.
