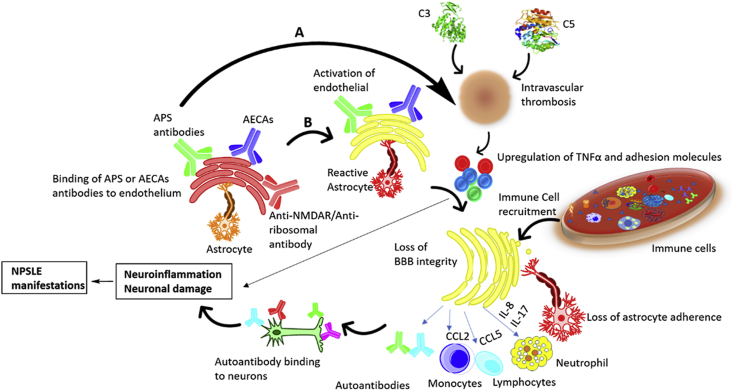
Fig. 1.
Role of cytokines and autoantibodies in NPSLE pathogenesis. A. Focal NPSLE: Antiphospholipid (APS) antibodies and complement components mediates the vascular mechanism resulting in the development of intravascular thrombosis and contribute to blood brain barrier dysfunction by upregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines, adhesion molecules and promoting reactive oxygen species formation. B. Diffuse NPSLE: Different antibodies, primarily anti-NMDAR, anti-ribosomal and anti-endothelial cell antibodies (AECAs) promote the upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and endothelial cell adhesion molecules that could result in the disruption of the endothelium of the blood brain barrier which allows extravasation of leukocytes to the central nervous system (CNS) ultimately inducing neural apoptosis and/or altered synaptic function.