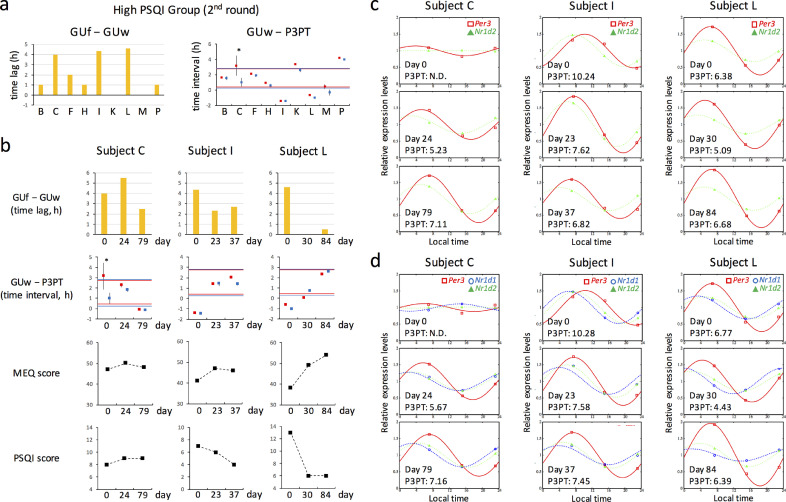
Fig. 4.
Validation of detection criteria for LCRSWD through follow-up investigations
(a) About two months after the assessment shown in Fig. 3, a second assessment was conducted for H-PSQI subjects with GUf − GUw > 2 h or GUw − P3PT < the mean – SD of the control group in the first assessment. Subjects M and P, who met neither of the criteria in the first assessment, were recruited as negative control subjects.
(b) Subjects C, I and L performed circadian amelioration for a period of several weeks (C, 24 days; I, 23 days; L, 30 days). They continued to perform circadian amelioration for as long as possible (C, 79 days; I, 37 days; L, 84 days, in total).
(a and b) GUf – GUw (yellow bars) and GUw − P3PT with 95% CI (dot plots) are shown for each subject. Red and blue dots indicate that P3PT was estimated based on expression of two and three clock genes, respectively. The 1 SD range of GUw − P3PT for the control group in Fig. 3 is again shown on these dot plots (red lines, estimation from 2 genes; blue lines, estimation from 3 genes).
(c and d) Clock gene expression rhythms of Subjects C, I and L before (day 0) and after circadian amelioration. A mathematical estimation of P3PT was performed based on the expression levels of two (c) or three clock genes (d). Coloured curves and dots represent estimated and experimental values, respectively. Estimated P3PT values are shown below the curves (N.D., not determined). (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)