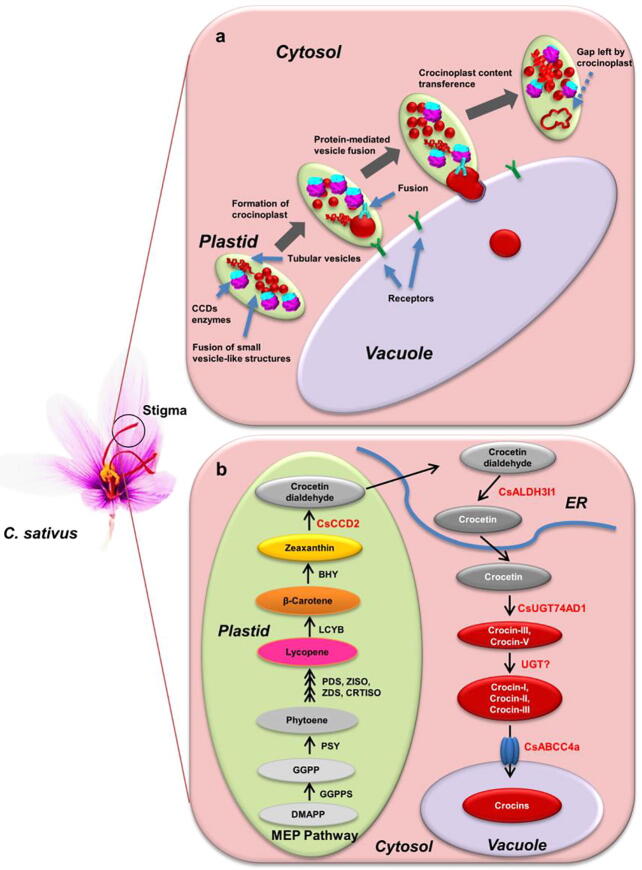
Fig 2.
Proposed models of subcellular routes for crocin compartmentation in stigmas of C. sativus. (a) Crocins are synthesized in the plastid, and then accumulated in plastid-localized small vesicle-like structures, which gradually fuse together to form crocinoplasts that could be directly transferred from the polarized end of the plastid to the vacuole. This is modified from Gomez-Gomez et al. 2017 [46]. (b) CsCCD2 cleaves zeaxanthin in the plastid to produce crocetin dialdehyde, which is further converted to crocetin by CsALDH3I1 in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). CsUGT74AD1 catalyzes the formation of crocins in the cytoplasm, and then crocins are transported into the vacuole through CsABCC4a. This is modified from Demurtas et al. 2018 [43].