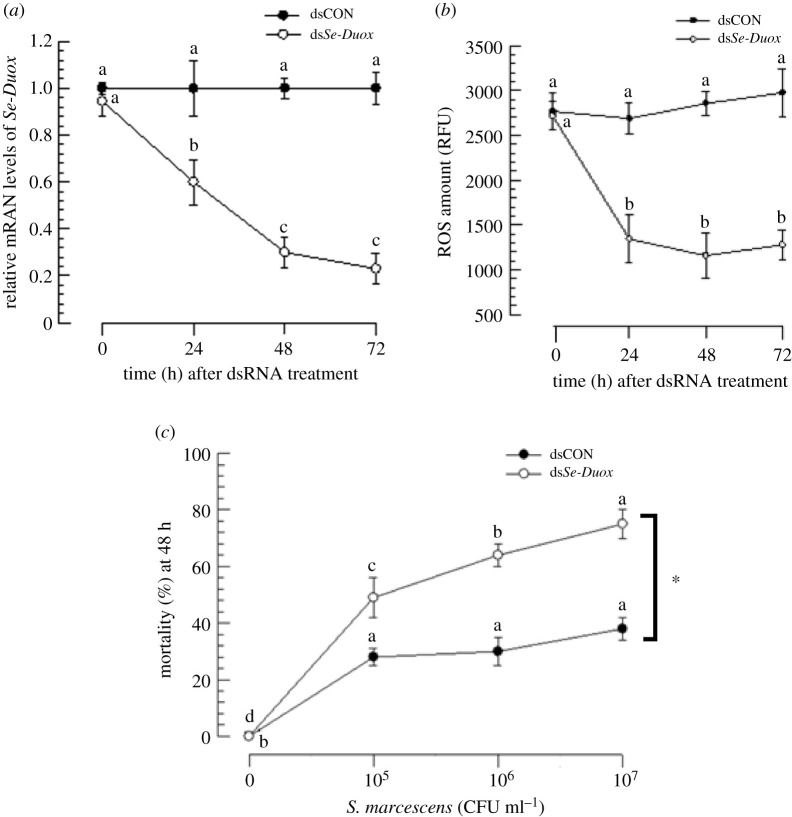
Figure 3.
RNAi of Se-Duox expression and subsequent influence on ROS level and larval susceptibility to S. marcescens. (a) Effects of RNAi on Se-Duox expression at different time points in midguts of S. exigua larvae (L5). One microgram of gene-specific dsRNA (dsSe-Duox) was injected into each larva. CpBV302, a viral gene, was used to generate control dsRNA (dsCON). (b) Inhibitory effects of RNAi specific to Se-Duox expression on total ROS levels in the midgut. To induce Duox expression and ROS, after dsRNA treatments, larvae were fed with E. coli (2 × 104 cells) treated artificial diet for 12 h. (c) Effects of Se-Duox RNAi on pathogenicity of S. marcescens against L4 larvae of S. exigua. RNAi-treated larvae were exposed to different concentrations of S. marcescens. Mortality was recorded at 48 h post feeding. Each treatment was replicated three times. Each replication used 10 larvae. Different letters above standard deviation bars indicate significant difference among means in each treatment and control at Type I error = 0.05 (LSD test). Asterisk indicates the statistical difference between control and treatment at 107 CFU ml−1 dose.