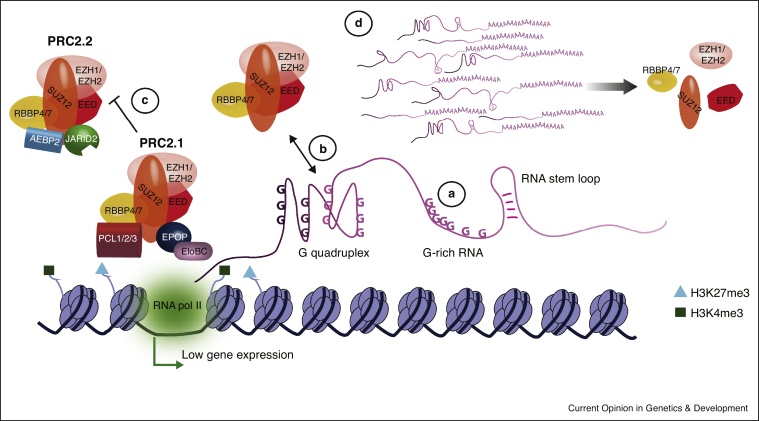
Figure 2.
PRC2-RNA interaction depends on RNA structure and composition modulating PRC2 function.
(a) PRC2 binds to RNA molecules promiscuously but its affinity varies with the sequence and folding of the RNA: G-quadruplex structures have the highest affinity for PRC2 binding, with unstructured G-rich RNA showing an intermediate binding affinity (contrary to A-rich RNA which binds minimally to PRC2) and RNA stem loops low affinity binding.
(b) PRC2 binds preferentially to G-quadruplex containing RNAs and these are able to compete with PRC2 binding to chromatin, resulting in its displacement and reduced H3K27me3 deposition. RNA binding to PRC2 can also directly inhibit its catalytic activity.
(c) PRC2.1 containing EPOP maintains a low level of gene expression at its target genes. Enrichment of EPOP-PRC2.1 and/or transcription keeps PRC2.2 further away from chromatin at these targets and prevents accumulation of H3K27me3 and complete gene silencing.
(d) Accumulation of nuclear pA+ RNAs in the absence of efficient RNA degradation by a nuclear RNA exosome-mediated pathway leads to destabilisation of the PRC2 complex.