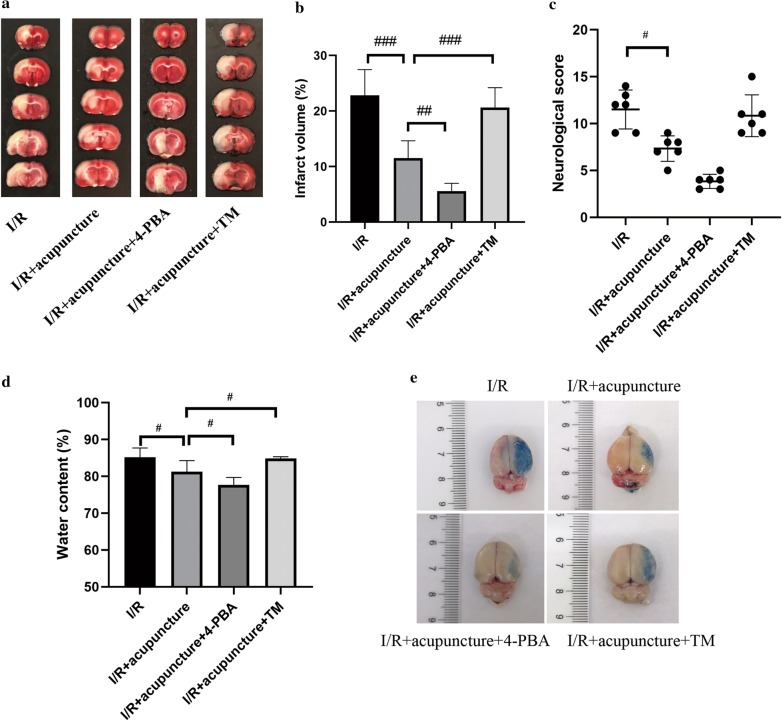
Fig. 7.
Acupuncture relieved cerebral ischemia–reperfusion (I/R) injury via suppressing endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. a, b The infarct volume of rats at 72 h after reperfusion in the four groups (I/R, I/R+ acupuncture, I/R+ acupuncture + 4-PBA, I/R+ acupuncture + tunicamycin (TM)) was detected by TTC staining. Brain infarct volume presented as a percentage of the infarct hemisphere. c The neurological deficits were determined by neurological score at 72 h after reperfusion. Neurological scores are presented as median (interquartile range). d Water content was determined. Results represent at least three independent experiments. e Blood brain barrier leakage was detected by Evans blue staining. Each experimental result was presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). #P < 0.05, ###P < 0.001 versus the indicated group