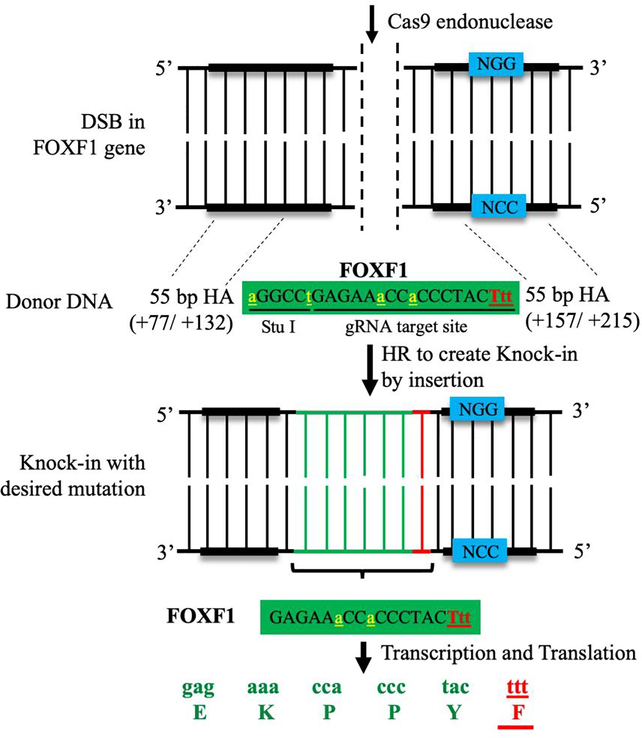
Figure 2: Generation of Foxf1WT/S52F knock-in mouse model of ACDMPV using CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing.
The schematic diagram shows the generation of Foxf1WT/S52F knock-in mice by homology-directed repair method. Single amino acid substitution of serine-52 (S52) to phenylalanine (F) is performed using a donor DNA template containing 55 nucleotide base pairs (bp) homology arms (HA) on either side of the template. HAs allow the donor DNA template to recombine into the host genome through homologous recombination (HR), inserting the S52F Foxf1 mutation. The mutated amino acid and triplet nucleotide codon (F/Ttt) are labeled in red, whereas endogenous nucleotides are labeled in green. Silent mutations (yellow) are inserted into the donor DNA template to create a new Stu I restriction site needed for identification of the S52F Foxf1 mutant allele.