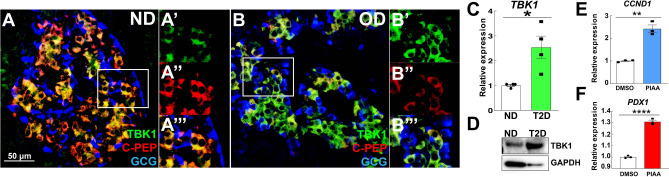
Figure 8.
TBK1 expression is elevated in β-cells of patients with type 2 diabetes. (A–B′′′) Confocal images of adult human pancreatic tissues [A–A′′′: non-diabetic (ND); B–B′′′: obese type 2 diabetic (OD)], stained for TBK1 (green), C-Peptide (red), and Glucagon (blue), showing higher TBK1 expression with lower levels of C-Peptide expression in β-cells of type 2 diabetic patients (N = 2 donors) than non-diabetic controls (N = 3 donors). Magnified images of TBK1 expression in β-cells (white squares in A and B) are shown in A′–A′′′ and B′–B′′′, respectively. Scale bar: 50 µm. (C) RT-qPCR analysis of TBK1 mRNA expression in non-diabetic controls (N = 4 donors) versus type 2 diabetic patients (N = 4 donors). Triplicate per donor. (D) Representative Western blot showing increased TBK1 expression in type 2 diabetic patient (N = 1 donor). (E,F) RT-qPCR analysis of cell cycle regulator CCND1 (E) and β-cell gene PDX1 (F) in vehicle- versus PIAA-treated type 2 diabetic islets. Triplicate (N = 1 donor). Gene expression was normalized to that of GAPDH and presented as fold changes (± SEM) against control expression; Unpaired two-tailed t test. Asterisks indicate statistical significance: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001.