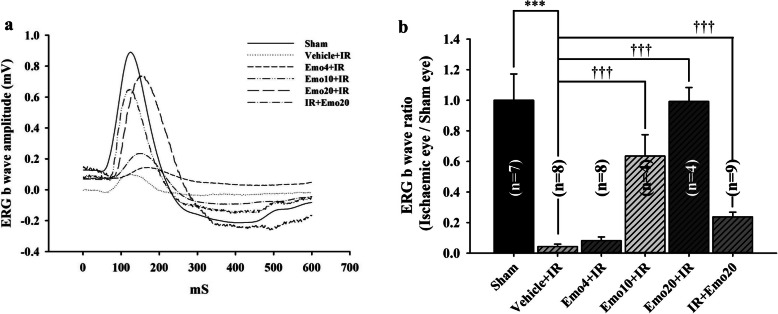
Fig. 2.
Summary of ERG b-wave measurement. a. Electroretinogram (ERG) b-wave amplitude. After ischemia/reperfusion (IR), a substantially reduced ERG b-wave amplitude was demonstrated in the ischemic retina pre-administered with intravitreous vehicle (Vehicle+IR) as compared with the control retina (Sham). In a dose-dependent way, pre-administered intravitreous emodin [4, 10 and 20 μM, i.e. Emo4 + IR, Emo10 + IR and Emo20 + IR], but not vehicle, ameliorated the ischemia induced reduction in ERG b-wave amplitude. Post-ischemic intravitreous injection of 20 μM emodin (IR + Emo20) also had an anti-ischemic effect. b. The analysis of ERG b-wave ratios revealing the efficacy of pre-ischemic and post-ischemic administration of emodin on the ischemic retinas. As compared to the ERG b-wave ratio of the Control (Sham = 0.82 ± 0.14: normalized to 1; n = 7), a significant (***; P < 0.001) reduction in that of the Vehicle+IR group was revealed. In contrast to the Vehicle+IR group (0.04 ± 0.01; n = 8), pre-ischemic intravitreous injection of emodin dose-responsively (Emo4 + IR = 0.08 ± 0.02, n = 8; Emo10 + IR = 0.64 ± 0.14, n = 4; then, Emo20 + IR = 0.99 ± 0.09, n = 4) and significantly (†††; P < 0.001; Emo10 + IR; Emo20 + IR) attenuated ischemic insult. Post-ischemic intravitreous injection of 20 μM emodin (IR + Emo20 = 0.24 ± 0.03; n = 9) had a significant (†††; P < 0.001) anti-ischemic effect, too. Data are mean ± S.E.M. of the number of animals shown in the parenthesis. Abbreviations for group names are provided in Table 2