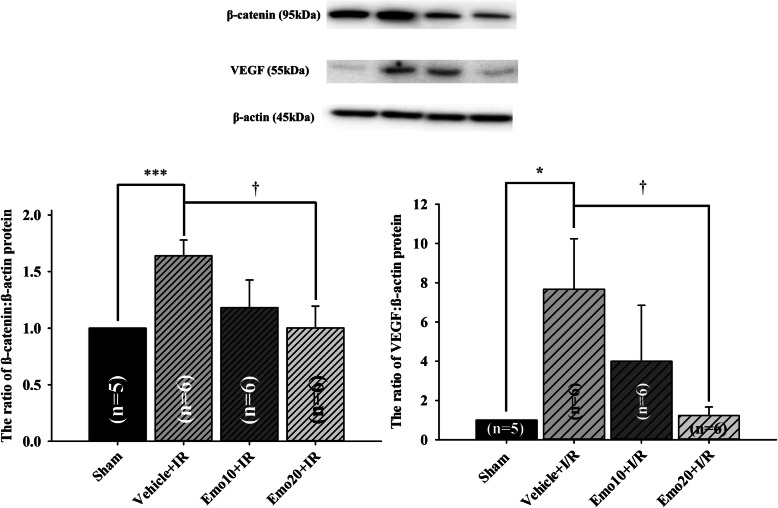
Fig. 5.
Western blot assay. Upper: blotting images of β-catenin, vascular endothelium growth factor (VEGF) and β-actin protein. Lane 1 is from a sham retina (Control); Lane 2 is the vehicle-pretreated ischemic retina (Vehicle+IR); Lanes 3 and 4 are from retinas that were subjected to IR and were pretreated with 10 μM (Emo10 + IR) and 20 μM emodin (Emo20 + IR). Lower: the bar chart analyzing the ratio of β-catenin/VEGF to the house-keeping protein β-actin. The ratio of the Sham group was normalized to 1. ***/* represents an extremely significant (P < 0.001) or a significant (P < 0.05) difference as compared to the Sham group. † represents a significant (P = 0.02/0.03) difference when compared to the Vehicle+IR group. As compared to the sham group, a significant increase in β-catenin/VEGF protein levels was observed after an ischemic insult and pre-ischemic application of vehicle (Vehicle+IR = 1.64 ± 0.14/7.67 ± 2.57). In contrast, pre-ischemic application of emodin dose-dependently and significantly (P = 0.02/0.03 at 20 μM; Emo20 + IR = 1.00 ± 0.19/1.23 ± 0.44) inhibited ischemia induced increase in β-catenin/VEGF protein levels. The values are mean ± S.E of the number of animals illustrated in the parenthesis. Abbreviations are listed as follows. IR: ischemia plus reperfusion; Pre-ischemic emodin 10 μM followed by IR (Emo10 + IR); Pre-ischemic emodin 20 μM followed by IR (Emo20 + IR). Abbreviations for group names are provided in Table 5