Figure 1.
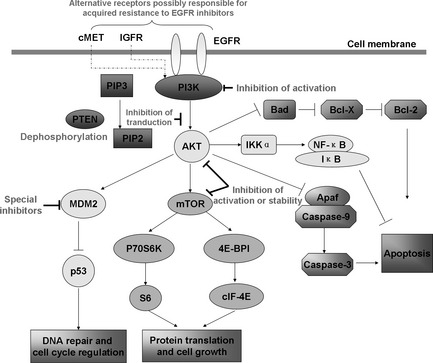
Mechanism of PI3K/Akt pathway to induce radioresistance and possible strategies to prevent acquired resistance to radiation through inhibiting the activity of relative elements. In the PI3K/Akt pathway, after GFR protein tyrosine kinases are activated, PI3K protein is recruited to the membrane by directly binding to phosphotyrosine consensus residues of growth factor receptor, leading to allosteric activation of the catalytic subunit. This activation results in production of the second messenger phosphatidylinositol‐3,4,5‐trisphosphate (PIP3). The lipid product of PI3K recruits Akt signaling protein domains to the membrane. Once activated, Akt mediates the activation of several targets, including IKKα, mTOR, MDM2 protein and Bad, Apaf/Caspase 9 proteins downregulation, and then results in cellular survival, growth and proliferation through various mechanisms. Possible strategies to prevent acquired resistance include combination therapy against alternate receptors, including cMET, IGFR and EGFR in the membrane and intracellular signal elements containing PI3K, AKT and mTOR.
