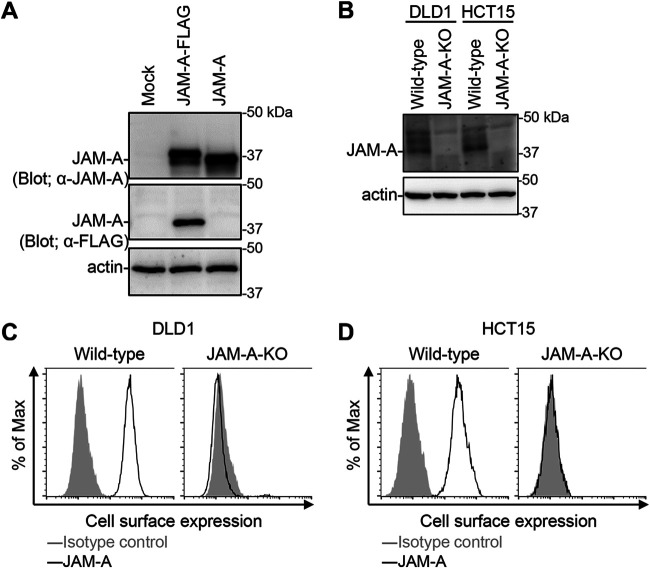
FIG 4.
Generation of JAM-A knockout cell lines. (A) Detection of JAM-A protein expression using mouse antiserum. Human 293T cells were transfected with pCXN2-JAM-A-FLAG and pCXN2-JAM-A. The cells were lysed with RIPA buffer and the lysates were centrifuged to remove cell debris. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with antiserum against JAM-A and antibodies specific for FLAG and β-actin. The molecular weights of the proteins are shown in kilodaltons (kDa). (B) Expression of JAM-A in JAM-A-KO cell lines. Cells were lysed with RIPA buffer and centrifuged to remove cell debris. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with antiserum against JAM-A and with an anti-β-actin antibody. The molecular weights of the proteins are indicated in kDa. (C and D) Cell-surface expression of JAM-A by wild-type and JAM-A-KO cell lines. DLD1 (C) and HCT15 (D) cells were collected in a nonenzymatic solution and then stained with mouse antiserum against JAM-A and an Alexa488-conjugated secondary antibody, followed by flow cytometry analysis.