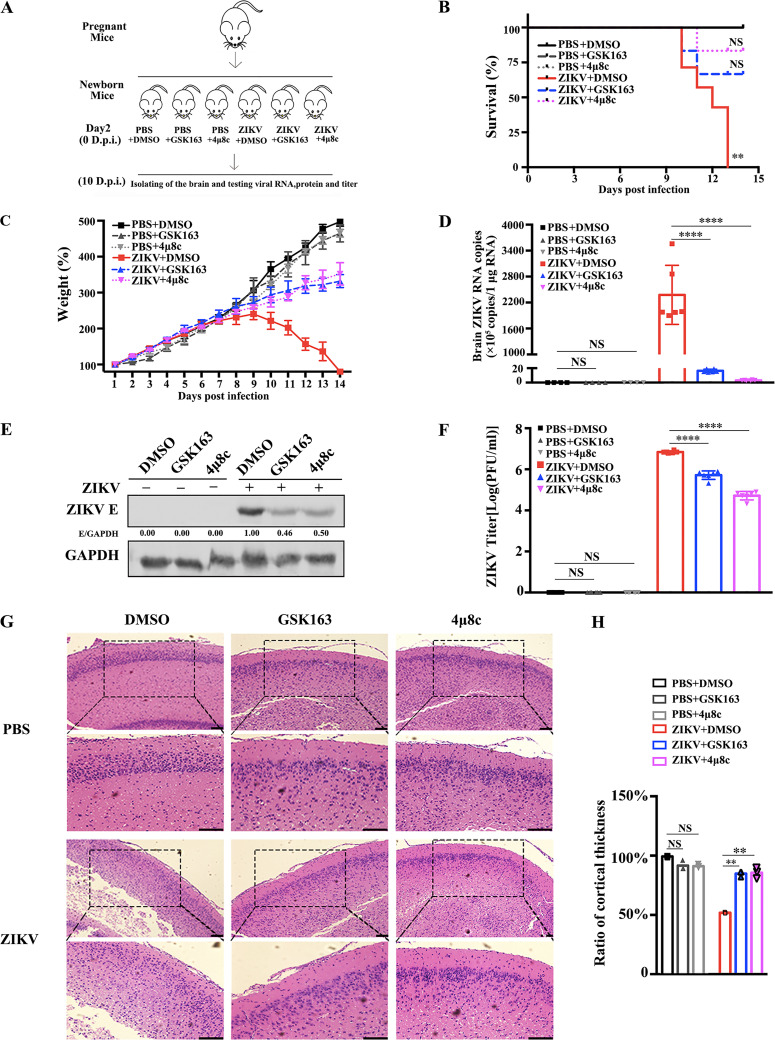
FIG 7.
IRE1α inhibitors suppress viral replication in ZIKV-infected Kunming neonatal mice. (A) An experimental scheme of the effect of IRE1α inhibitors in the ZIKV-infected neonatal mouse model. Kunming neonatal mice were treated with 1 mM GSK163 or 4μ8c (DMSO as the control) by intracerebral inoculation on day 2 after birth. Then, they were intracerebrally inoculated with 4 × 104 PFU of ZIKV suspension at 1 h posttreatment. Mock-infected controls were inoculated with the same volume of PBS. (B) Survival curves of neonatal mice injected with intracerebral inoculation under different treatment conditions (n = 6). Kaplan-Meier survival curves were analyzed by the log rank test. **, P < 0.01. (C) Changes in mouse weight were calculated daily. The weight changes were compared using one-way ANOVA. Error bars indicate standard errors of the means. (D to F) ZIKV replication levels in mouse brain tissues. The brains of neonatal mice were isolated at 10 days p.i. for the detection of viral replication levels. Viral RNA copies (D), viral protein levels (E), and viral titers (F) were determined by qRT-PCR, Western blotting, and plaque assay, respectively. Viral RNA copies were expressed as viral RNA equivalents per microgram upon comparing with a standard curve produced by gradient 10-fold dilutions of ZIKV RNA. (G) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of mouse brain tissues was performed, and the cortical radial thickness is indicated with bars (10 μm). Coronal sections of cerebral cortex marked by dashed squares were magnified two times and shown below (scale bar, 20 μm). (H) Quantification of the above-described sample cortex thickness by ImageJ software. The thickness of the control cortex was normalized to 1. Data are representative of those from three independent experiments. **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001 (two-tailed Student t test).