Figure 1.
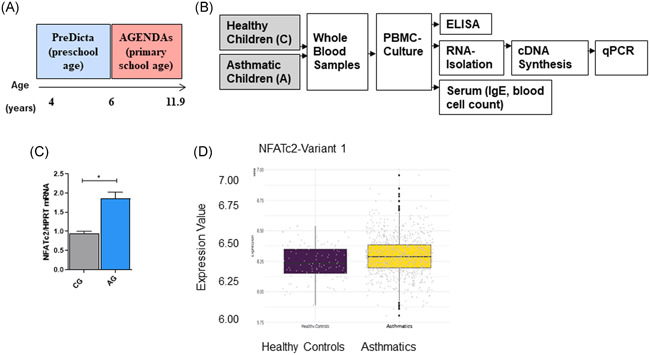
NFATc2 is induced in PBMCs of preschool children as well as in peripheral blood cells from asthmatic children and adults with allergic asthma. (A) Age range in the PreDicta cohort compared with AGENDAs. In the PreDicta cohort we examined children at preschool age. (B) Experimental design of the PreDicta and AGENDAs studies (C) NFATc2 mRNA measured by qPCR in untreated PBMCs isolated from the PreDicta cohorts: control group (CG); n = 2 and asthma group (AG); n = 10. p = .0125 unpaired t‐test. (D) Increased mRNA expression of NFATc2 in peripheral blood of asthmatic children and adults compared with healthy controls in Asthma Bridge and CAMP cohorts. We used microarray gene expression data from the Asthma Biorepository for Integrative Genomic Exploration (Asthma BRIDGE, N = 1448) and Childhood Asthma Management Program (CAMP, N = 620). The shorter isoform A (variant 1) of NFATC2 was significantly overexpressed in peripheral blood from asthmatics (n = 865) compared with nonasthmatic, healthy controls (n = 865 vs. n = 116, respectively; fold‐change = 1.043, p = .02). Statistical Significance as indicated: *p ≤ .05; **p ≤ .01; ***p ≤ .001. CAMP, Childhood Asthma Management Program; cDNA, complementary DNA; ELISA, enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay; mRNA, messenger RNA; NFATc2, nuclear factor of activated T cells c2; PBMCs, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; qPCR, quantitative polymerase chain reaction
