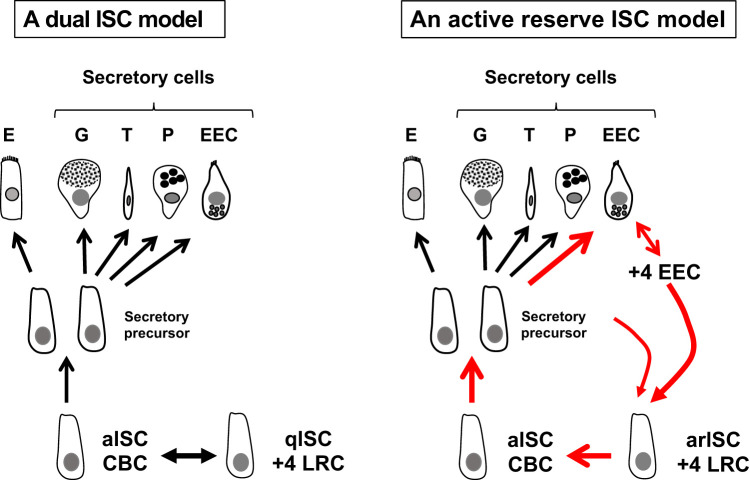
Fig. 1.
Models of small intestinal stem cell dynamics. Crypt-based columnar cells (CBCs) serve as actively cycling intestinal stem cells (aISCs) and generate all the differentiated descendants of the intestinal epithelium, including enterocytes (E), goblet cells (G), tuft cells (T), Paneth cells (P), and enteroendocrine cells (EEC). Left, a dual ISC model. ISC homeostasis is maintained by aISCs in coordination with coexisting quiescent ISCs (qISCs) identified as +4 label-retaining cells [LRCs, also recently referred to as reserve ISC (rISC)]. Right, an active reserve ISC (arISC) model. ISC homeostasis is maintained by aISCs and complemented by arISC. A subset of secretary cell precursors and +4 EECs, coincident with +4 LRCs, serve as +4 arISCs to form a dynamic loop contributing to the ISC pool.