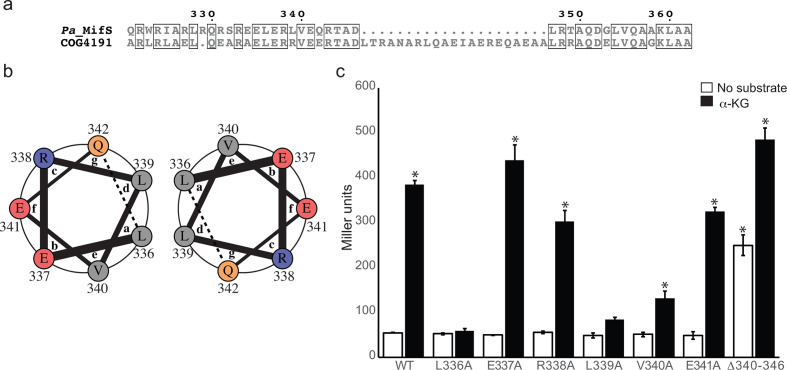
Fig. 6.
Linker domain involved in MifS α-KG response. (a) Alignment of cytoplasmic linker domain sequences of MifS and COG4191 (DctB family consensus sequence). Positions with identical residues are boxed. Alignment was generated using clustal Omega [56] and displayed using ESPript 3.0 [57]. (b) Helical wheel representation of one heptad of the linker domain spanning from residue 336 to residue 342. The interactions between the a position L336 and the d position L339 of two adjacent helices are demonstrated by the helical wheel representation, generated using DrawCoil 1.0 (http://www.grigoryanlab.org/drawcoil). (c) Mutations were introduced into the linker domain of MifS. The wild-type mifS gene or one of the mutated mifS genes were introduced into E. coli cells harbouring the mifR gene and the PPA5530::lacZ reporter. Cells were grown in LB media to an OD600 value of 0.3 and challenged with α-KG or no substrate. LacZ expression levels were measured 60 min post-induction. Data points represent mean values±the standard deviations (n=3). Analysis of variance was performed by using Dunnett’s post-hoc test (α value of 0.05) to identify significant differences (P<0.0001; marked with an asterisk).