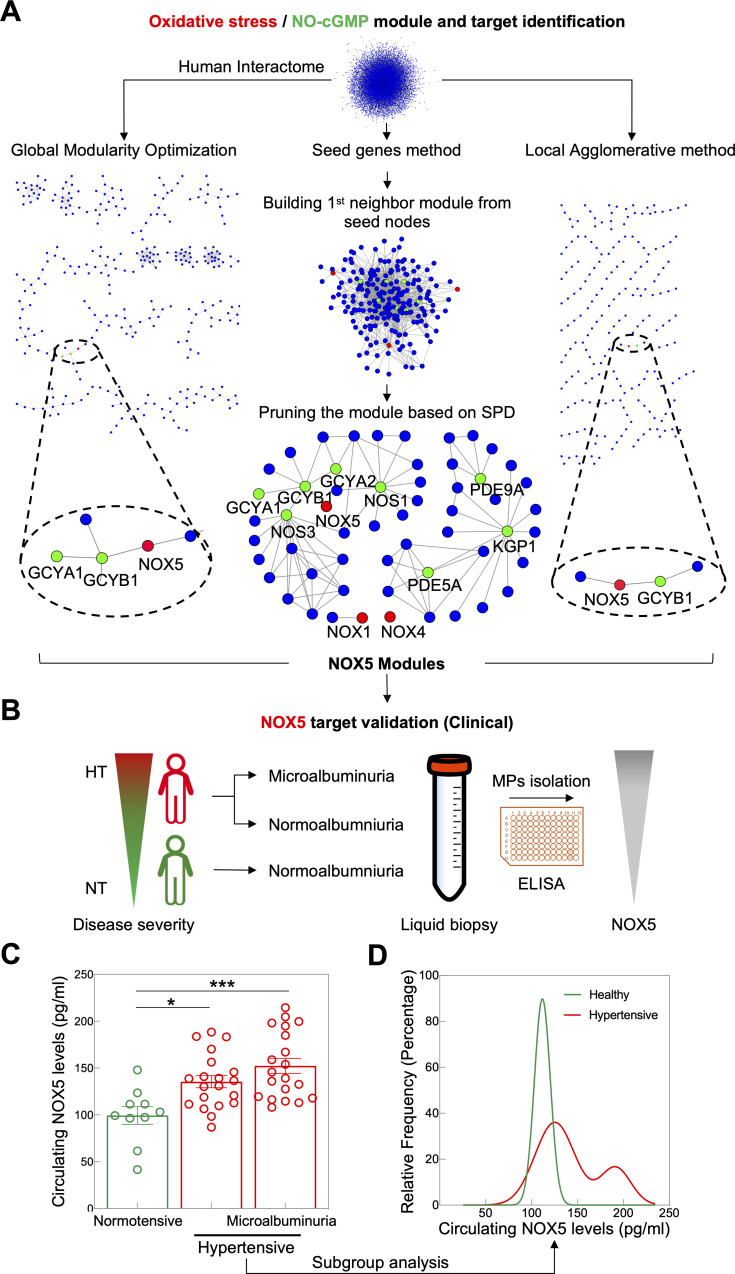
Fig 1. Identification of NOX5 as direct neighbor of endothelial NO-cGMP signaling and clinical validation in hypertension.
(A) NOX module was constructed by first neighbor subnetwork pruned based on SPD (the middle panel) where NOX isoforms (red nodes) and NO-cGMP related proteins (green nodes) were used as seed nodes. The resulting NOX module was confirmed with 2 disease module identification methods, global modularity optimization (the left panel) and the agglomerative local method (the right panel). All the methods identified NOX5 as the closest link to NO-cGMP signaling and excluded NOX1–4. (B) NOX5 levels in endothelial microparticles (MPs) isolated from plasma of NT, normoalbuminuric individuals and HT normoalbuminuric and microalbuminuric patients were measured by ELISA. (C) NOX5 levels were increased in HT patients with normoalbuminuria (n = 20) compared to NT individuals (n = 10). NOX5 levels were even higher in HT patients with microalbuminuria (n = 20). Comparison between groups was done by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. (D) Subgroup analysis of all HT patients shows a bimodal distribution (p = 0.0007, two-tailed F-test, adjusted r2 = 0.9973), where only the right but not the left subgroup peak of HT patients has NOX5 levels that are significantly different from the healthy individuals. All data are represented as mean ± SEM of n independent experiments *p = 0.014, ***p = 0.0003. All raw data are included in the S1 Data file. cGMP, cyclic GMP; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; GCYA, soluble guanylate cyclase alpha; GCYB, soluble guanylate cyclase beta; HT, hypertensive; KGP1, cGMP-dependent protein kinase 1; MP, microparticle; NO, nitric oxide; NOS, NO synthase; NOX, NADPH oxidase; NT, normotensive; PDE, phosphodiesterase; SPD, subnetwork-participation-degree.