Figure 1. Optogenetic tools for remote activation of intracellular Ca2+ signaling.
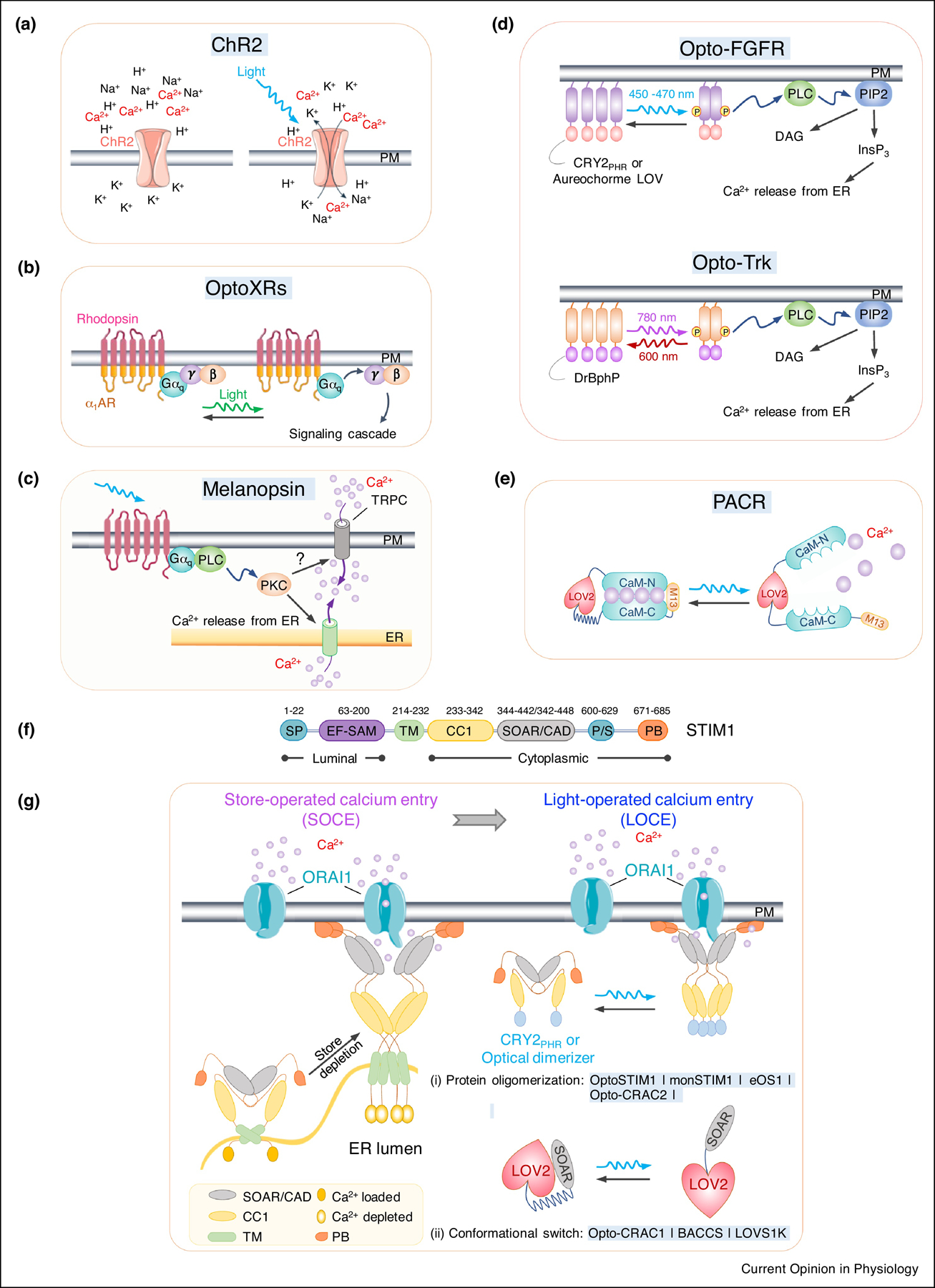
a. Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) as a cation-permeant channel is non-selective toward H+, K+, Na+, and Ca2+.
b. OptoXRs as light-sensing rhodopsin-GPCR chimeras. The extracellular and TM regions are derived from a light-sensitive rhodopsin, while intracellular regions from different adrenergic receptors (β2AR or α1AR).
c. Blue light-mediated isomerization of the light-absorbing retinal cofactor triggers the conformation change of melanopsin (OPN4) and subsequent activation of Gαq-phospholipase C (PLC) to induce Ca2+ influx via TRPC channel.
d. Opto-RTKs as photoactivatable membrane-anchored receptor tyrosine kinases. The intracellular domain of RTKs (FGFR or TrK), is fused to CRY2 or other optical dimerizers, thereby enabling light-inducible clustering to activate downstream signaling, including the PLC pathway and subsequent Ca2+ mobilization.
e. LOV2-CaM-M13 hybrid protein as a photoactivatable Ca2+ releaser (PACR). Photostimulation results in the release of bound Ca2+ into the surrounding environment.
f. Domain architecture of STIM1. SP, signal peptide; EF, EF-hand Ca2+-binding motif; SAM, sterile alpha motif; TM, transmembrane domain; CC1, coiled-coil domain 1; SOAR, STIM-Orai activating region; PS, proline-serine rich domain; PB, polybasic domain.
g. Genetically-encoded Ca2+ channel actuators (GECAs) derived from STIM1.
(Left) schematic illustrating functional STIM1-ORAI1 coupling in response to store depletion. Ca2+ depletion within the ER lumen induces oligomerization of the luminal EF-SAM domain to initiate STIM1 activation and triggers conformational switch to expose SOAR/CAD and the C terminal PB domain. Next, STIM1 undergoes further oligomerization and migration toward the PM, a process facilitated by the association between SOAR/CAD and ORAI1, as well as the interaction between positively-charged PB and negatively-charged phosphoinositides embedded in PM. SOAR/CAD is responsible for direct engagement and activation of ORAI channels to mediate Ca2+ influx.
(right) Optogenetic engineering to convert store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) into light-operated Ca2+ entry (LOCE). (i) A protein oligomerization-based engineering strategy using various optical dimerizers (Opto-CRAC2) and CRY2-STIM1 fusion proteins (OptoSTIM1, monSTIM1, and eOS1). Upon light illumination, CRY2 or optical dimerizers undergoes oligomerization, mimicking Ca2+ -depletion induced EF-SAM multimerization in ER lumen, to trigger STIM1 activation and the subsequent opening of ORAI Ca2+ channels in the PM. (ii) The design of GECAs based on LOV2 conformational switch (Opto-CRAC1, LOVS1K or BACCS), in which the CC1-SOAR interaction-mediated intramolecular autoinhibition is mimicked by LOV2-SOAR fusion in the dark. Upon photostimulation, LOV2 undergoes conformational changes to expose SOAR/CAD, which engages PM-resident ORAI Ca2+ channel to induce Ca2+ influx.
