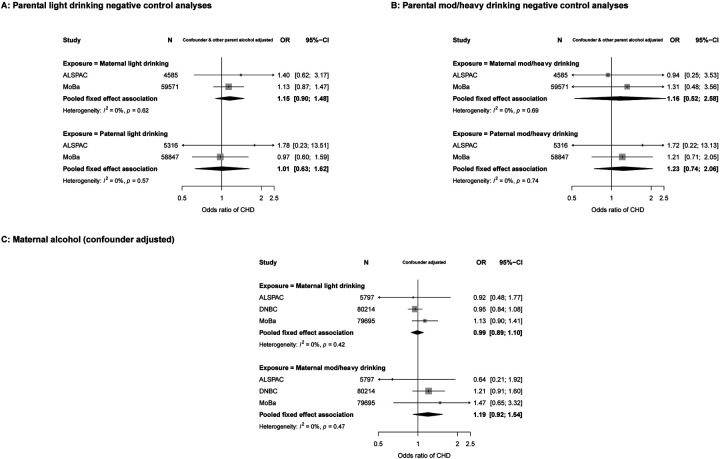
Figure 3.
Associations in each study and pooled across studies for maternal and paternal pregnancy alcohol intake and offspring CHDs. Figure 3A shows confounder and other parent’s alcohol adjusted odds ratios of any CHD for maternal light drinking during pregnancy (top graph) and paternal light drinking (bottom graph). Figure 3B shows confounder and other parent’s alcohol adjusted odds ratios of any CHD for maternal moderate/heavy drinking during pregnancy (top graph) and paternal moderate/heavy drinking (bottom graph). 64,156 mothers with 524 CHD cases and 64,163 fathers with 529 CHD cases were included in the alcohol negative control analyses shown (3A & 3B). Figure 3C shows confounder adjusted odds ratios of any CHD for maternal light drinking during pregnancy (top graph) and maternal mod/heavy drinking (bottom graph) (165,706 mothers with 1,823 CHD cases). Confounders (depending on cohort): maternal and paternal age, education, ethnicity, smoking, maternal parity, offspring sex (and other parental alcohol intake in panels A & B).