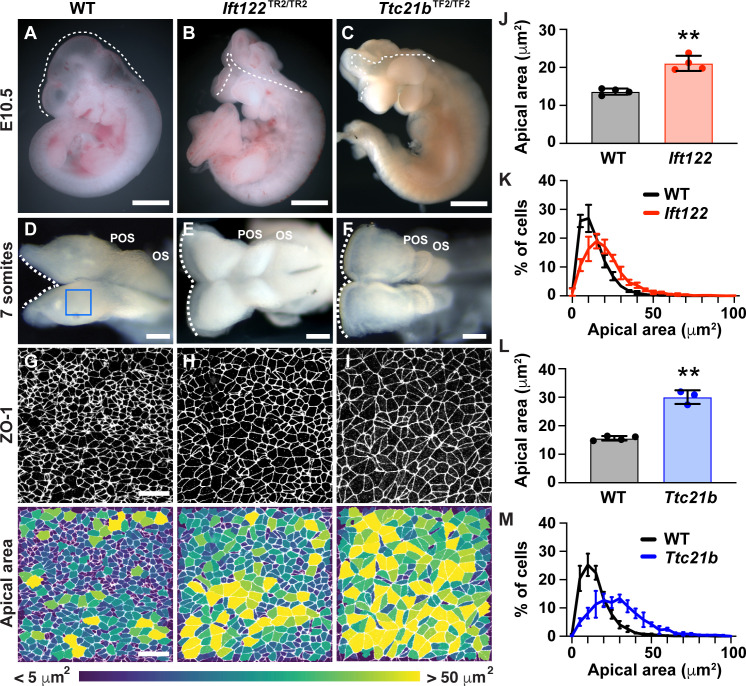
Figure 4. IFT-A proteins have an early role in cranial neural tube closure.
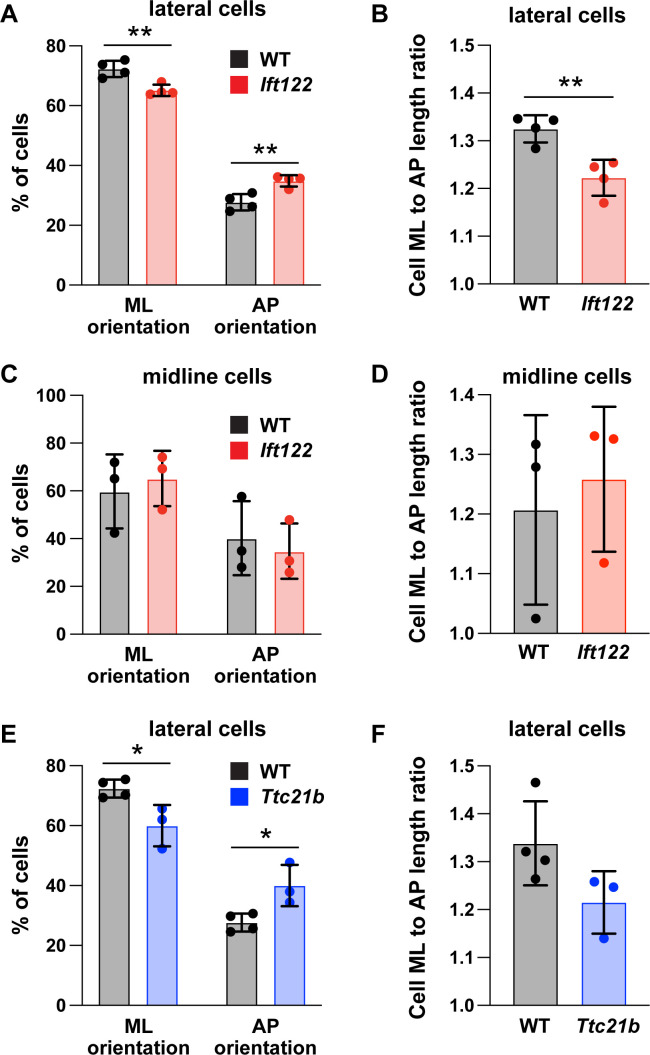
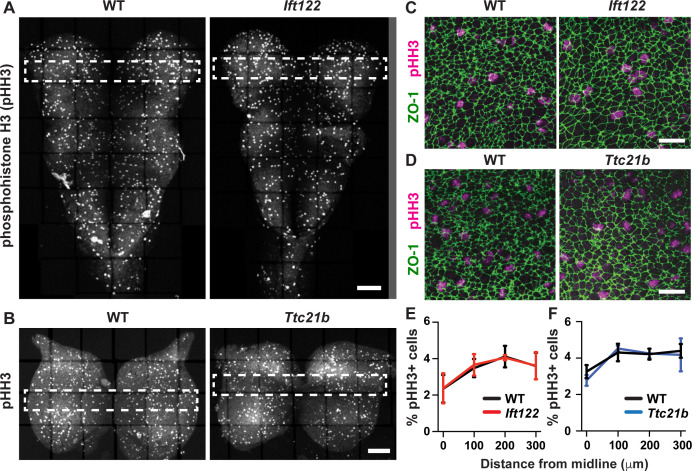
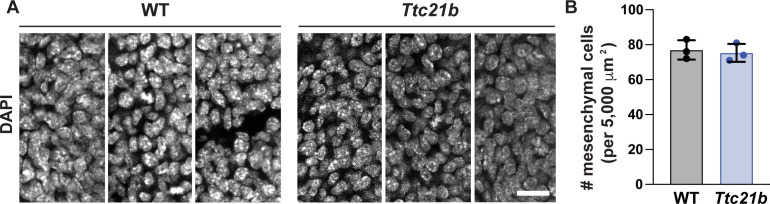
(A) Wild-type littermate control (WT) showing normal cranial closure. (B,C) Exencephaly was observed in 10/10 Ift122 mutants (B) (compared with 0/16 WT controls) and 5/5 Ttc21b mutants (C) (compared with 0/13 WT controls). Dashed lines, lateral edge of the cranial neuroepithelium. (D–F) The cranial neural folds fail to elevate in Ift122 (E) and Ttc21b (F) mutants compared to WT controls (D). Box, region shown in (G–I). (G–I) Lateral cells in WT and mutant embryos. Cells are labeled with ZO-1 (top) and are color-coded by apical area (bottom). (J–M) Average apical cell area (J,L) and apical area distributions (K,M) of lateral cells in Ift122 and Ttc21b mutants compared with WT controls. A single value was obtained for each embryo and the mean ± SD between embryos is shown, n = 3–4 embryos/genotype, **p<0.01 (Welch’s t-test). See Supplementary file 1 for n and p values. Anterior up in (A–C) and (G–I), anterior left in (D–F). Bars, 1 mm (A–C), 100 μm (D–F), and 20 μm (G–I).