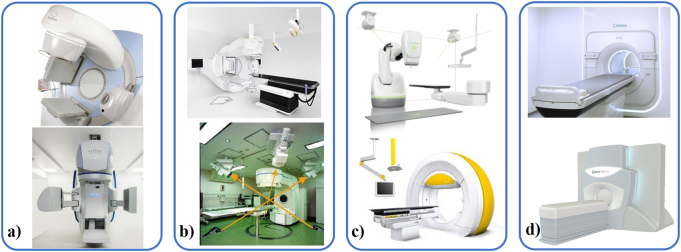
Figure 2.
Systems for internal motion monitoring during RT delivery are shown. (a) Elekta (Elekta AB, Stockholm Sweden) (top, image courtesy of Elekta) and Varian (Varian Medical Systems, Palo Alto, CA) (bottom, image provided courtesy of Varian) standard linacs with a deployed MV imager opposite the treatment head and a perpendicularly mounted kV imaging system. (b) BrainLab ExacTrac (BrainLab AG, Feldkirchen, Germany) with stereoscopic kV imaging and external breathing monitoring (top, here mounted on an Elekta linac) and the RTRT system with four kV imaging systems (bottom, reproduced from https://rad.med.hokudai.ac.jp/en/research/treatment/tracking/ with permission). (c) The robotic CyberKnife® (Accuray Inc, Sunnyvale, CA) system and Vero Gimbal (BrainLab and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Japan) incorporate stereoscopic kV imaging and external breathing monitoring. (d) Unity (top, image courtesy of Elekta) and MRIdian (Viewray Inc, Cleveland, OH) (bottom) are the two commercially available MR-guided linacs (see section 2.5).