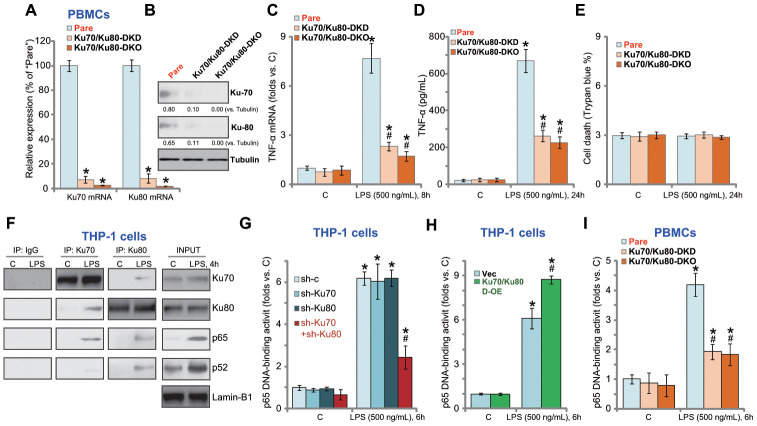
Figure 4.
Ku70 and Ku80 silencing or KO inhibits LPS-induced pro-inflammatory cytokines production and NFκB activation in human PBMCs. The primary PBMCs were transfected with Ku70 shRNA lentivirus plus Ku80 shRNA lentivirus (“Ku70/Ku80-DKD”), or lenti-CRISPR/Cas9-Ku70 KO construct plus lenti-CRISPR/Cas9-Ku80 KO construct (“Ku70/Ku80-DKO”), expression of listed genes was shown (A and B); Cells were treated with LPS (500 ng/mL) or vehicle control (“C”) for indicated time, TNF-α mRNA expression and protein content in the culture medium were tested by qRT-PCR (C) and ELISA (D); Cell death was tested by Trypan blue staining assay (E); The relative NFκB activity was tested by p65 DNA-binding assay (I). THP-1 cells were treated with LPS (500 ng/mL) for 4h, nuclear lysate proteins were subjected to co-immunoprecipitation assay (“IP: Ku70/Ku80”) and Western blotting assay (“INPUT”) (F). Stable THP-1 human macrophages, bearing control shRNA lentivirus (“sh-c”), Ku70 shRNA lentivirus (“sh-Ku70”) and/or Ku80 shRNA lentivirus (“sh-Ku80”) (G), as well as the Ku70-expressing AAV plus the Ku80-expressing AAV (“Ku70/Ku80 D-OE”) or empty vector (“Vec”) (H), were treated with LPS (500 ng/mL) or vehicle control (“C”) for 6h, the relative NFκB activity was tested by p65 DNA-binding assay. Expression of listed proteins was quantified, normalized to the loading control (B). Data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD, n=5). “Pare” stands for the parental control PBMCs (A–E, I). *p<0.05 vs. “C” treatment. # p<0.05. LPS treatment of control cells. Experiments in this figure were repeated four times, and similar results were obtained.