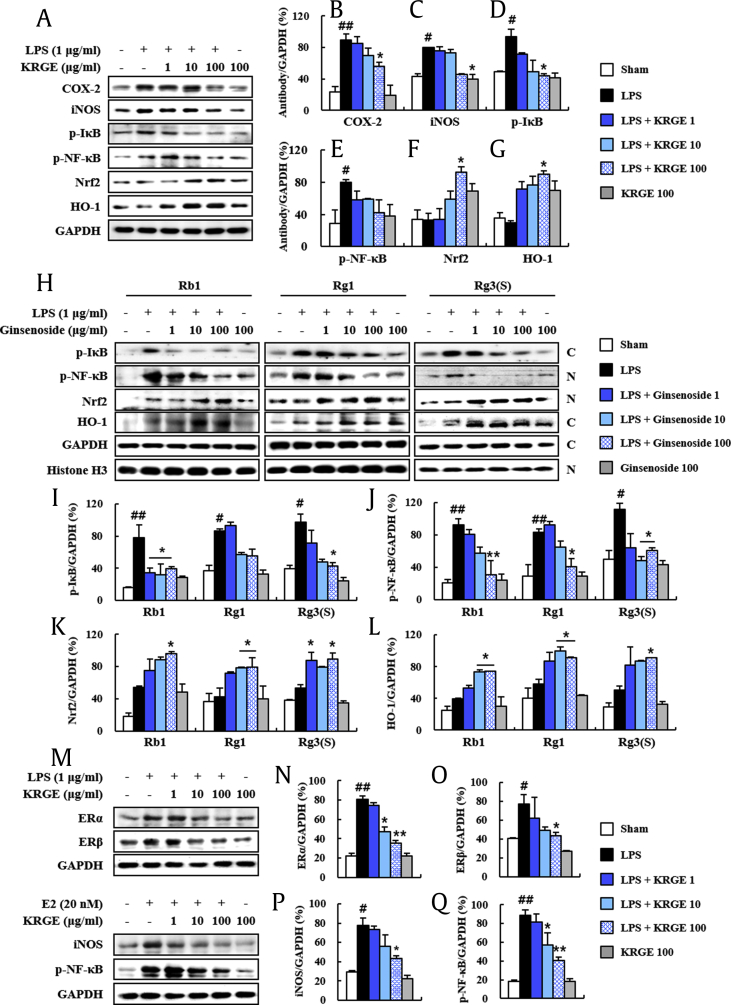
Fig. 5.
Antiinflammatory and antioxidant effects of KRGE in the lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 cells. (A-G) Levels of activation of inflammatory and antioxidant mediators in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 cells were measured by immunoblot analysis (A) and quantified (B-G). COX-2 (B), iNOS (C), p-IkB (D), p–NF-kB (E), Nrf2 (F), and HO-1 (G). (H-L) Levels of activation of inflammatory and antioxidant mediators in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 cells following treatment with ginsenosides (Rb1, Rg1, and Rg3(S)) were measured by immunoblot analysis (H) and quantified (I-L). Cytosolic p-IkB (I), nuclear p–NF-kB (J), nuclear Nrf2 (K), and cytosolic HO-1 (L). (M-P) Protein expression of ERα, ERβ, iNOS, and p–NF-kB in the lipopolysaccharide or E2-stimulated RAW264.7 cells following treatment with KRGE were measured by immunoblot analysis (M) and quantified (N–P). ERα (N), ERβ (O), iNOS (P), and p–NF-kB (Q). The C and N in the photo H display cytosolic and nuclear extracts, respectively. Values represent the mean ± SEM. #p < 0.05 and ##p < 0.01 versus vehicle-treated group; *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.05 versus lipopolysaccharide-treated or E2-treated group. KRGE, Korean Red Ginseng extract; SEM, standard error of mean; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cell; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid–derived 2-related factor; HO-1, antiheme oxygenase-1; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; ER, estrogen receptor.