Figure 2. Effects of methionine metabolism on T cell function and tumor immunity.
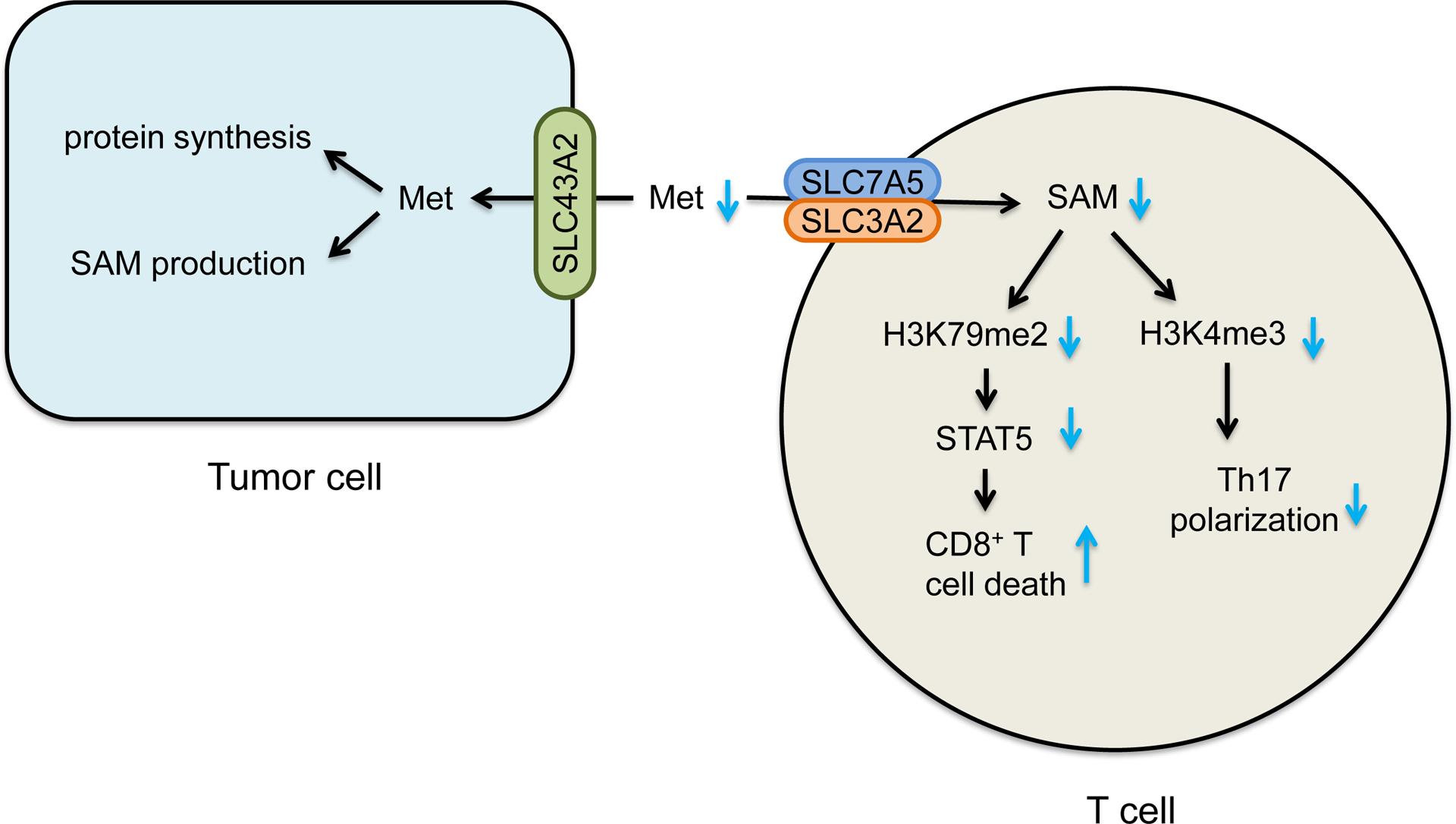
Methionine metabolism generates a universal methyl donor S-adenosyl-methionine (SAM). Tumor cells express high levels of SLC43A2 and consume methionine in the tumor microenvironment. This results in insufficient methionine and SAM for T cells - thus causing loss of CD8+ T cell H3K79me2 and STAT5 expression and function, and impairing H3K4me3 and Th17 polarization.
