Figure 3. Role of arginine and Try-Kyn metabolisms in tumor immune evasion.
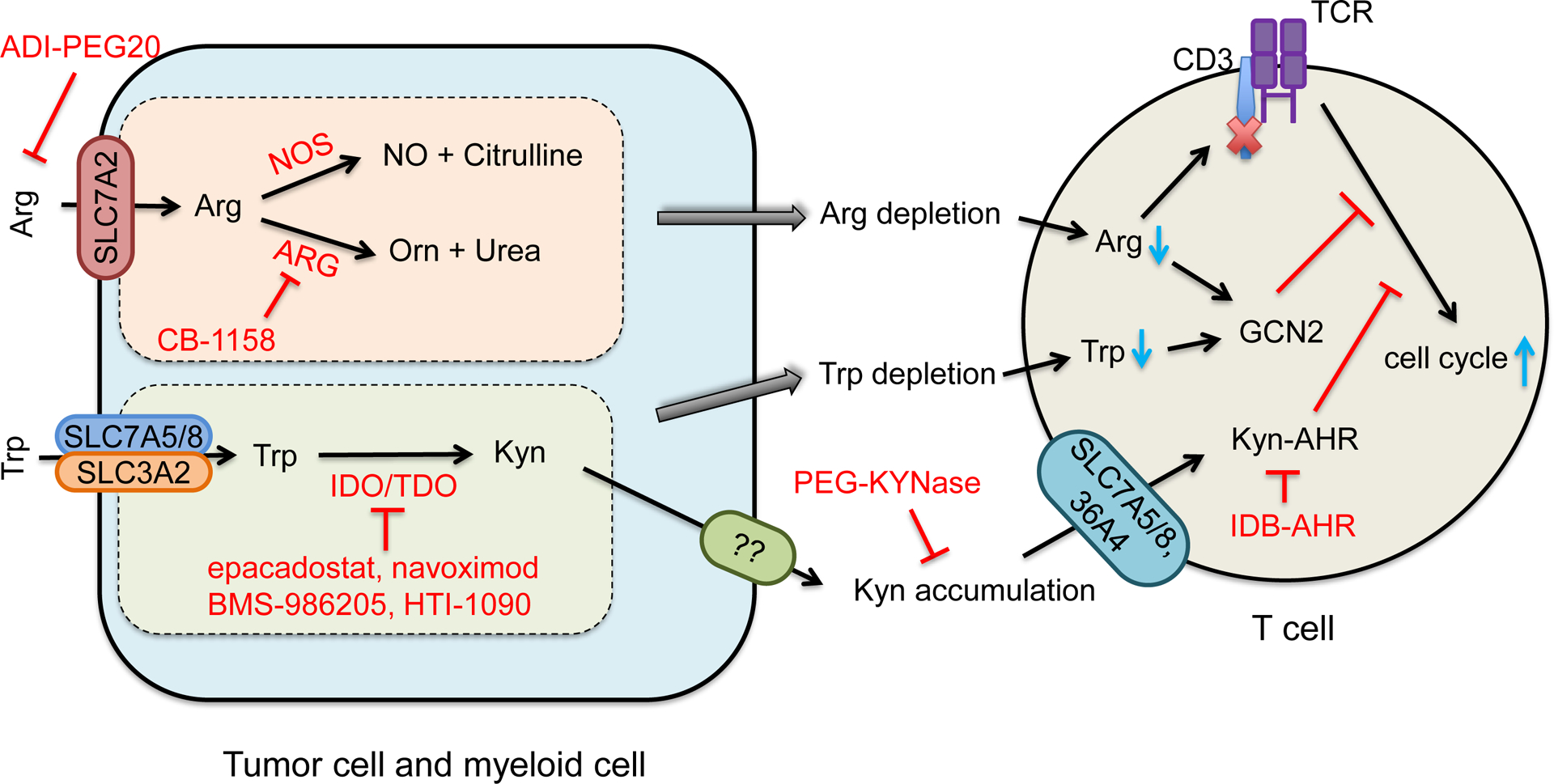
Arginine (Arg) is transported by SLC7A2. Intracellular Arg metabolism results in extracellular Arg depletion and NO production. Arg deficiency impairs and NO inhibits T cell function.
Trp is transported by SLC3A2 and SLC7A5 or SLC7A8. Trp is catalyzed by indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) or tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase (TDO) to become kynurenine (Kyn). Trp-Kyn metabolism results in extracellular Trp depletion and Kyn accumulation, subsequently causing T cell inhibition.
Arginine deiminase (ADI-PEG20) degrades arginine. PEG-KYNase degrades Kyn. Small inhibitors that target key enzymes in Arg and Trp-Kyn metabolic pathways are listed in red.
