Fig 5 |. Hypotonic gelling formulation (12% Hypo) provides therapeutically relevant delivery of sunitinib malate (SM, 0.4% w/v) to the posterior segment with once-daily dosing in rabbits and pigs.
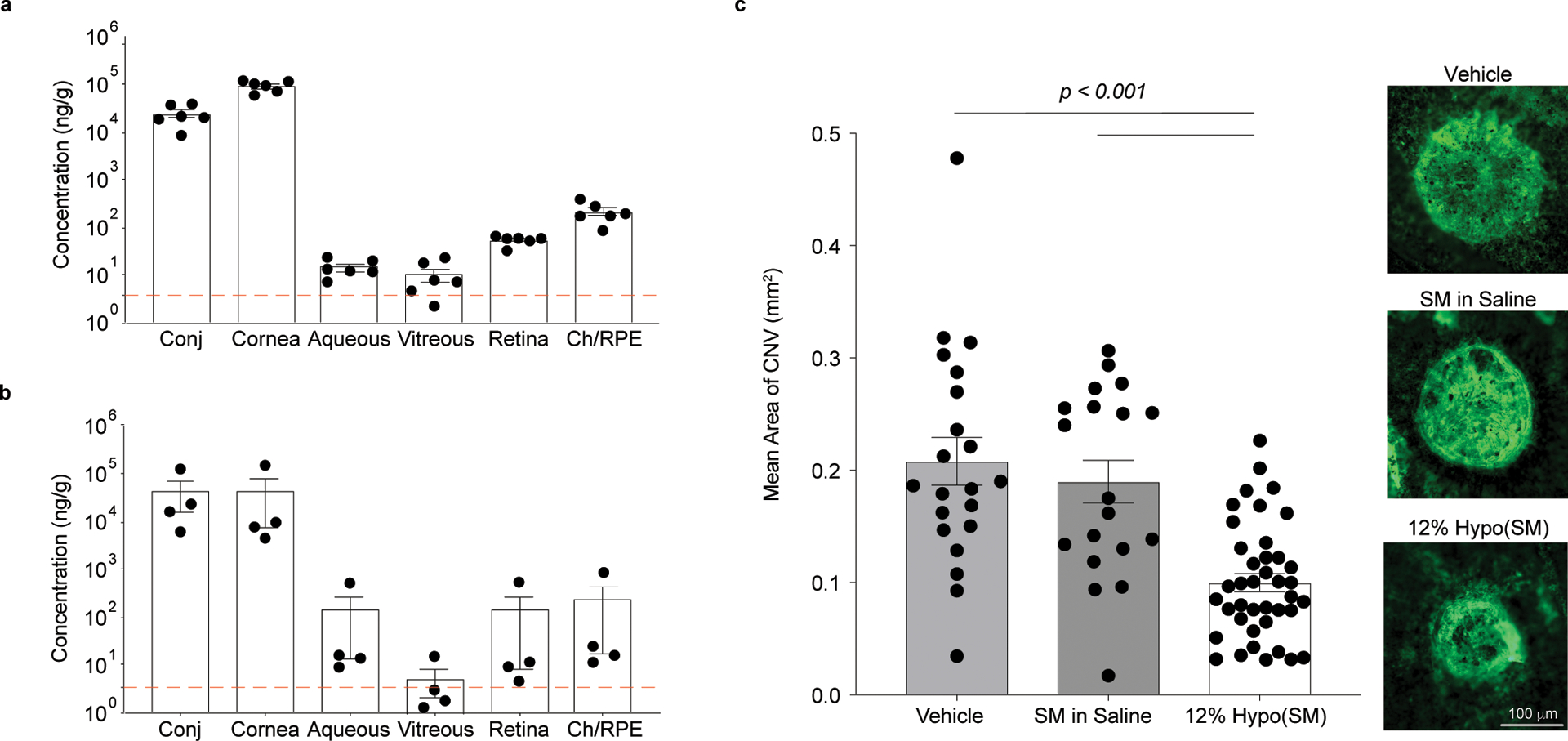
a, Dutch belted rabbits were dosed unilaterally with 12% Hypo(SM) once daily for 14 days. Ocular tissues were collected 6 h after the last dose (n = 6 independent animals). Combined levels of sunitinib and N-desethyl sunitinib are shown with a dotted line indicating the Ki for VEGFR/PDGFR. b, Juvenile Yorkshire pigs received 12% Hypo(SM) once daily for 5 days unilaterally. Ocular tissues were collected 1 h after the last dose (n = 4 independent eyes). Combined levels of sunitinib and N-desethyl sunitinib are shown with a dotted line indicating the Ki for VEGFR/PDGFR. Drug concentrations achieved in the retina and choroid/retinal pigmented epithelium (Ch/RPE) exceed the inhibitory concentration. c, Laser-induced rupture of Bruch’s membrane was performed in Juvenile Yorkshire pigs and each pig received either 12% Hypo(SM), SM dissolved in saline (SM in Saline), or 12% Hypo vehicle (Vehicle) bilaterally. Topical eye drops were given daily for a total of 15 days. Right panels show fluorescent images of CNV spots with areas representative of the means for each group. Scale bar = 100 μm and applies to all images. The 12% Hypo(SM) (n = 40 CNV spots and one image was obtained per CNV spot) provided a significant reduction in mean area of CNV compared to 12% Hypo vehicle (Vehicle) (n = 21 CNV spots and one image was obtained per CNV spot) or SM in Saline (n = 19 CNV spots and one image was obtained per CNV spot). Statistical analyses conducted by linear mixed model. Data shown as mean ± SEM.
