Figure 2. CD26 identifies a population of collagen-expressing fibroblasts in adult human dermis.
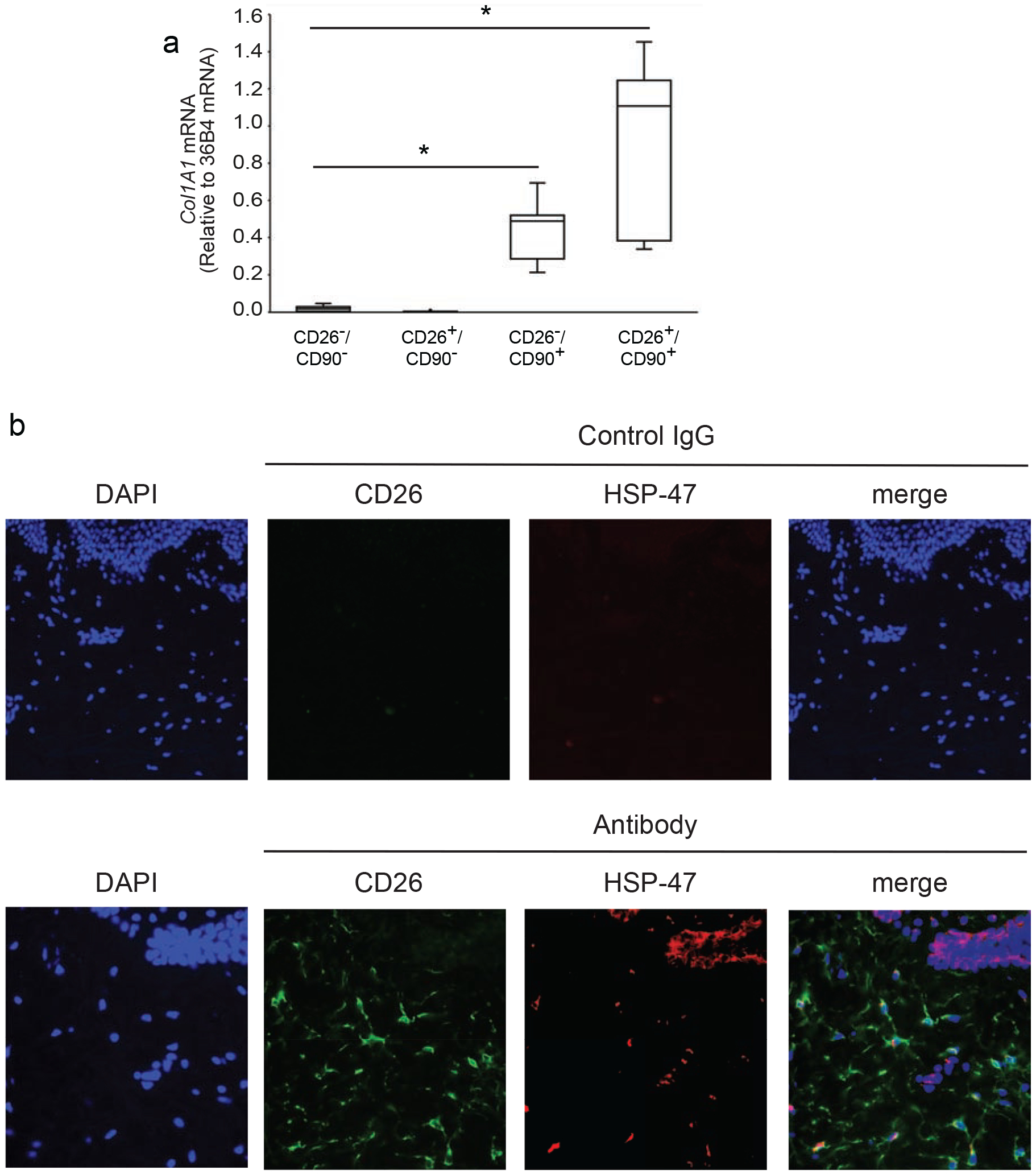
A) Dermal cells were prepared from buttocks skin by collagenase digestion and sorted by FACS, as described in the Figure 1 legend. Total RNA was prepared from each of the four indicated cell populations and type I collagen (COL1A1) gene expression was determined by real-time PCR. Data are normalized to internal control housekeeping gene 36B4. Results are means+SEM, n=5 biological, n=2 technical replicates: *p<0.05 vs CD26−/CD90− or CD26+/CD90+. B) Localization of CD26+ fibroblasts in the dermis of adult human skin. Paraformaldehyde-fixed human skin sections were double-immunostained for CD26 (green) and HSP-47 (red). HSP-47 is a chaperone for collagen and serves as a marker for collagen-producing cells. Nuclei were stained blue with DAPI. CD26+/HSP-47+ double-positive cells (closed arrows) and CD26+ single positive (open triangles) cells are observed in the dermis. In addition, HSP-47+ staining is observed in basal keratinocytes (open arrows), which express basement membrane collagen. Representative images from five experiments (40x objective). Scale bars are 50 microns.
