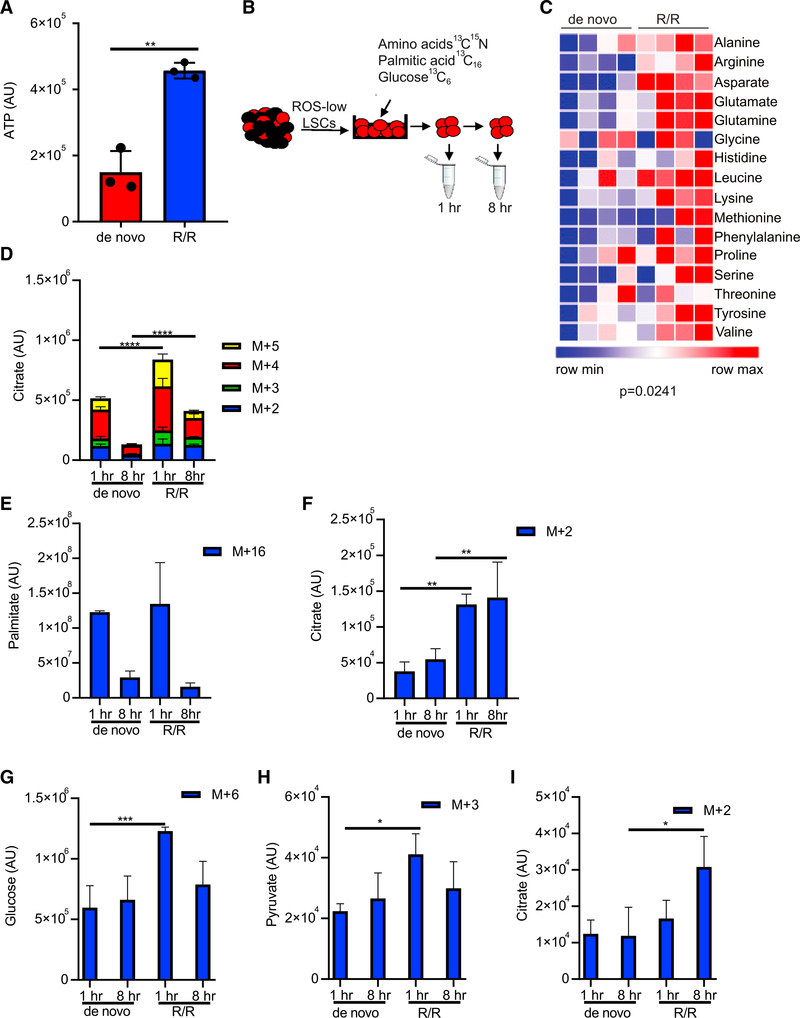
Figure 2. R/R LSCs Have Increased Energy Metabolism Compared with De Novo LSCs.
(A) ATP levels from LSCs isolated from 3 de novo and 3 R/R AML patients determined by mass spectrometry. AML specimens used in this analysis include AML1– AML6. Statistical significance was determined using an unpaired Student’s t test.
(B) Schematic of experimental design. LSCs were isolated from de novo and R/R AML patient specimens and then incubated with [13C6] glucose, 13C15N amino acids, or[13C16] palmitic acid for 1 or 8 h. Metabolites were then measured by mass spectrometry.
(C) Heatmap of 13C15N amino acids in de novo and R/R LSCs after a 1-h incubation. Statistical significance was determined using a paired Student’s t test. AML2 and AML5 were used in this analysis.
(D) TCA cycle intermediate citrate metabolized from 13C15N amino acids.
(E) Palmitic acid uptake from [13C16 palmitic acid.
(F) TCA cycle intermediate citrate metabolized from [13C16 palmitic acid. (G) Glucose uptake from [13C6] glucose.
(G) lucose uptake from [13C6] glucose.
(H) Pyruvae metabolized from [13C6] glucose.
(I) TCA cycle intermediate, citrae metabolized from [13C6] glucose.
(D–I) Statistical significance determined by two-way ANOVA, and AML2 and AML5 were used in the analysis. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.005, ****p < 0.001.