Figure 1: Epigenetic and Neuroprotective mechanisms of KD therapy.
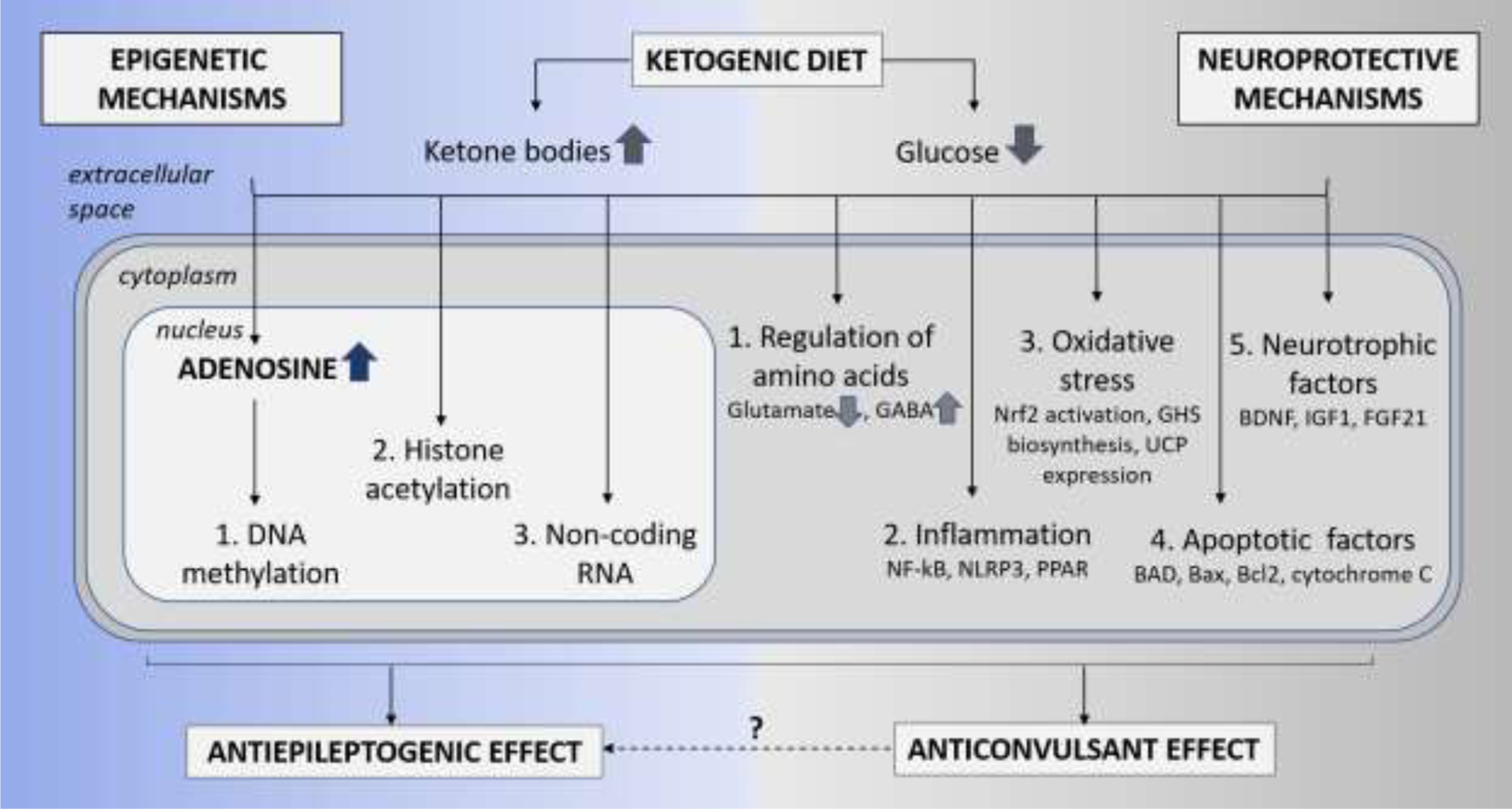
The schematic is a simplistic representation of the two broader mechanisms thought to play a critical role in the neuroprotective and antiepileptogenesis functions of the KD therapy. The epigenetic mechanisms include restoration of (1) DNA methylation, (2) histone acetylation, and (3) non-coding RNA. Whereas, the neuroprotective mechanisms include (1) regulation of amino acids resulting in reduced glutamate and increased GABA neurotransmitters, (2) reduction in inflammation and oxidative stress via activation of mediators such as NF-kB, NLRP3 and PPAR, (3) reduction in oxidative stress via activation of Nrf2 pathway, glutathione (GHS) biosynthesis and expression of uncoupling proteins (UCPs), (4) inhibition of apoptotic factors such as BAD, Bax, and cytochrome C, and (5) release of neurotrophic factors such as BDNF and FGF21.
