Figure 2. Histopathological and clinical findings following 0.02% MMC and vehicle control applications in rabbit corneas that had −9D PRK.
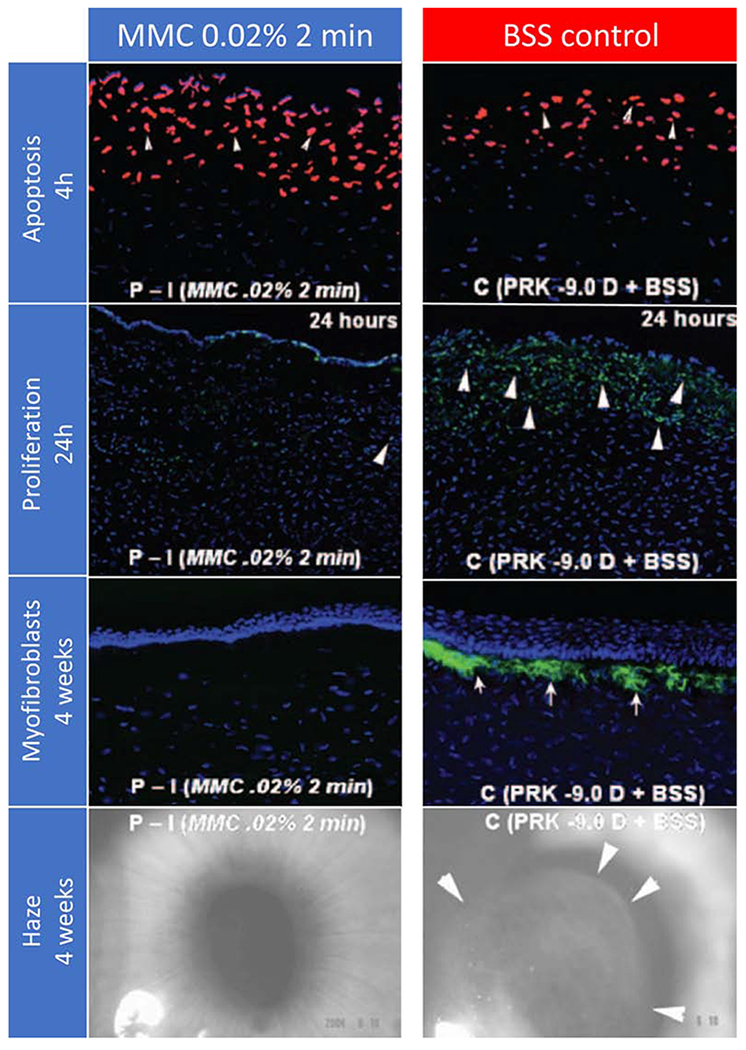
First row. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase biotin-dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay to detect fragmented DNA characteristic of apoptotic cells four hours after −9D PRK and 0.02% mitomycin C for 2 minutes or −9D PRK and vehicle balanced salt solution (BSS) application for 2 minutes in rabbits. Cell nuclei were stained blue with DAPI and TUNEL-positive cells stained red (arrows). There was a small but statistically significant increase in the number of cells undergoing apoptosis in the stroma in the mitomycin C group compared to the control group, with the cornea with the greatest level of apoptosis shown (original magnification 200 X). Second row. Immunohistochemistry for Ki-67 at 24 hours to detect cell mitosis in the central cornea of rabbit eyes that had −9 D PRK for myopia followed by mitomycin C 0.02% or vehicle application for 2 minutes after treatment. There was heavy cell mitosis (arrowheads) in the anterior stroma in the vehicle-treated group (C). Markedly reduced proliferation of cells in the anterior stroma was noted in corneas treated with 0.02% mitomycin C for 2 minutes (P-I). Third row. Immunohistochemical staining for the alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) marker for myofibroblasts in rabbit corneas that were treated with MMC 0.02% or vehicle BSS for 2 minutes after −9D PRK. Cells nuclei were stained blue with DAPI and α-SMA-positive myofibroblasts were stained green (arrows). Note that no myofibroblasts were seen in the MMC-treated corneas, whereas numerous α-SMA+ myofibroblasts were detected in all corneas in the BSS-treated group (original magnification 200X). Fourth row. Representative slit-lamp photographs show subepithelial haze patterns and locations restricted to the area of corneal ablation. Faint 0.5 subepithelial corneal haze is present in the prophylactic mitomycin C −9D PRK group P-I while Grade III subepithelial haze was present in all corneas in the prophylactic BSS-treated PRK group (C). Note that the subepithelial haze tends to terminate exactly at the margin of the excimer laser ablation (arrows in C) (original magnification 10X). Reprinted with permission from Netto et al. J. Refract. Surg. 2006;22:562–574.
