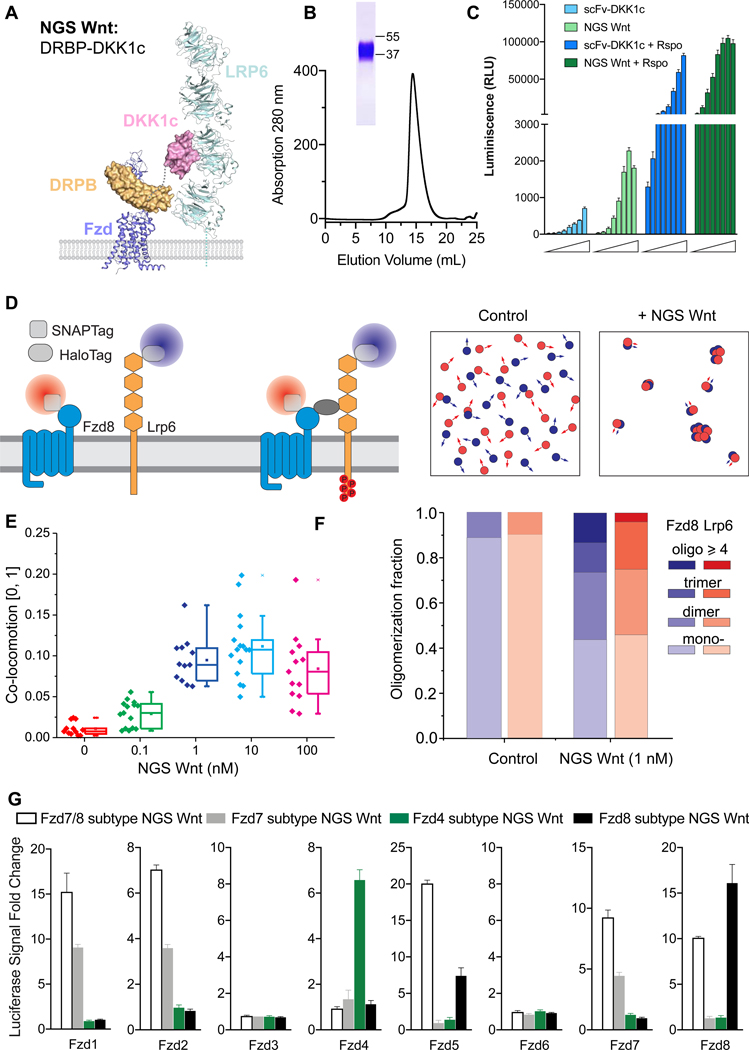
Figure 1. Design concept of NGS Wnt.
(A) Design schematic of NGS Wnt. Fzd subtype (purple) specific binder DRPB (orange) is fused with Lrp5/6 (cyan) binder DKK1c (pink) using a flexible Gly-Ser linker (grey dash line). Figure is adapted from PDBs (3S8V, 3S94, 6BD4 and 6NDZ).
(B) Size exclusion chromatography of Fzd7/8 subtype NGS Wnt. The band on SDS-PAGE gel represents Fzd7/8 subtype NGS Wnt.
(C) NGS Wnt (156 pM to 20 nM) induces higher β-catenin signaling change than scFv-DKK1c (2 nM to 250 nM) with or without Rspo (25 nM). Data represent mean and S.E., N = 3 technical replicates from representative experiment.
(D) Schematic for characterizing NGS Wnt induced heterodimer-/oligomerization ofFzd8 and Lrp6 by single molecule imaging in live cells.
(E) Co-locomotion Lrp6 and Fzd8 measured within 20 min after addition of NGS Wnt at indicated concentrations. N > 12 for each condition. Error bar represents mean and S.E.
(F) Quantification of Lrp6 and Fzd8 receptor oligomer fractions. Control refers tountreated samples. More than 2800 individual complex intensities were examined for each receptor.
(G) Fzd subtype NGS Wnts specifically induce β-catenin signaling in through targeted Fzd receptors. All data represents mean and S.E., N = 3 technical replicates from representative experiment.
See also Figures S1, S2 and Video S1 and S2.