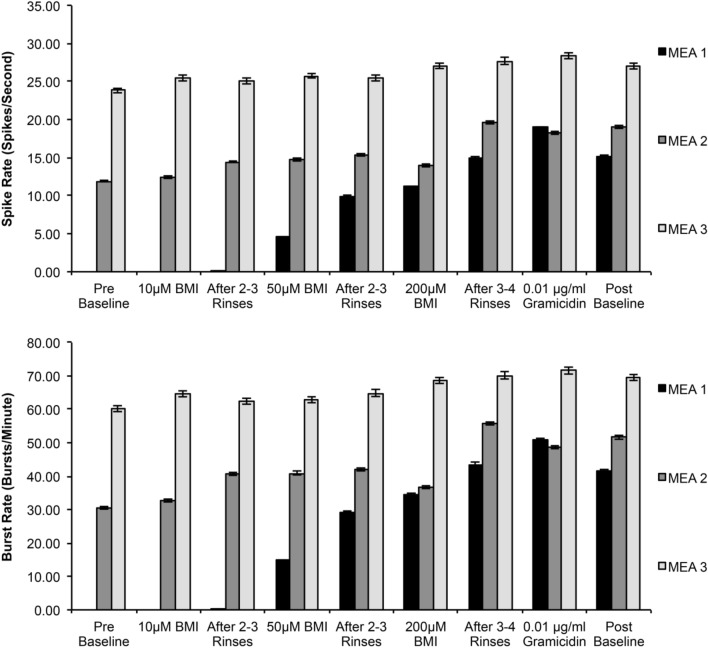
Fig. 4.
The electrophysiological response of 3-D neural co-cultures at 21 days in vitro to chemical perturbations via BMI and gramicidin in terms of changes in spike (a) and burst rates (b). BMI is expected to have an excitatory effect by blocking the inhibitory synaptic transmission, whereas gramicidin depolarizes neurons by creating ion-permissive pores in the plasmalemma. Note that the increase in electrophysiological activity of the cultures is in inverse proportion to base-line activity levels prior to chemical perturbation. Random network connectivity, differing inhibitory synapse numbers, and differing saturation limits for chemical excitation may explain the variability in response between the cultures. Rinses did not completely reverse the pharmacological effect indicating that the thickness and density of the cultures may limit chemical diffusion