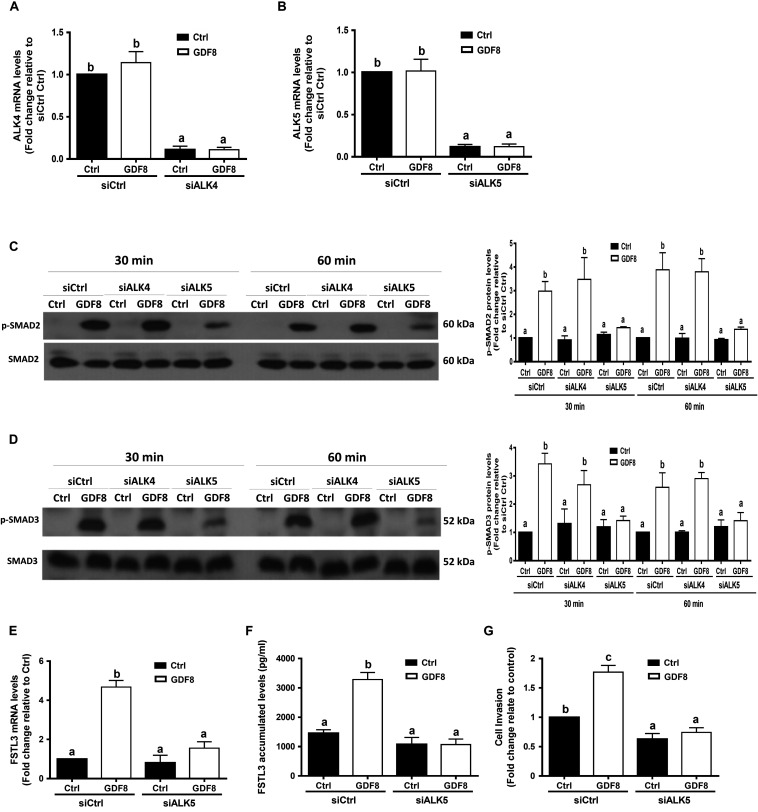
FIGURE 5.
ALK5 mediates the growth differentiation factor 8 (GDF8)-induced increase in phosphorylated protein levels of SMAD2/3 and cell invasion in HTR8/SVneo cells. (A,B) HTR8/SVneo cells were transfected for 24 h with 20 nM non-targeting control siRNAs (siCtrl), 20 nM siRNAs targeting ALK4 (siALK4) or 20 nM siRNAs targeting ALK5 (siALK5), after which the cells were treated with the vehicle control (Ctrl) or 25 ng/mL GDF8 for 24 h; the mRNA levels of ALK4 (A) and ALK5 (B) were examined using RT-qPCR. (C,D) HTR8/SVneo cells were transfected for 24 h with 20 nM siCtrl, 20 nM siALK4, or 20 nM siALK5, after which the cells were treated with the vehicle control (Ctrl) or 25 ng/mL GDF8 for 30 or 60 min; the phosphorylated protein levels of SMAD2 (C) and SMAD3 (D) were examined using western blot analysis. (E–G) HTR8/SVneo cells were transfected for 24 h with 20 nM siCtrl or 20 nM siALK5, after which the cells were treated with the vehicle control (Ctrl) or 25 ng/mL GDF8 for 24 h; the mRNA (E) and accumulated (F) levels of follistatin-like 3 (FSTL3) were examined using RT-qPCR and ELISA, respectively, and cell invasion was examined using the Matrigel-coated transwell assay. SMAD2 and SMAD3 were used as the loading control and references for densitometric analysis for p-SMAD2 and p-SMAD3, respectively. The results are displayed as the mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments, and the values with different letters are significantly different (P < 0.05).