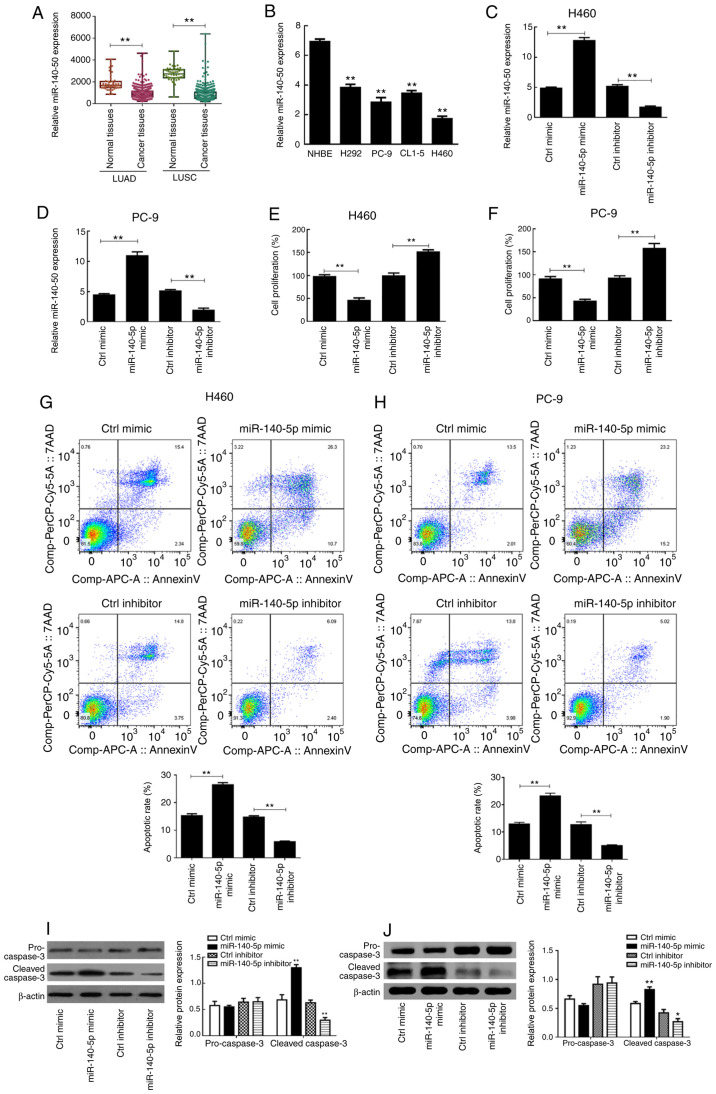
Figure 1.
miR-140-5p regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of human lung cancer cells. (A) miR-140 expression in normal tissues and cancer tissues from the LUAD and LUSC datasets downloaded from The Cancer Genome Atlas database. (B) Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR analysis was performed to detect miR-140-5p expression in lung cancer cell lines (H292, PC-9, CL1-5 and H460) and NHBE cells. The transfection efficiency of overexpressing or silencing miR-140-5p expression in (C) H460 and (D) PC-9 cells. The effect of overexpressing or silencing miR-140-5p expression on the proliferation of (E) H460 and (F) PC-9 cells. The effect of overexpressing or silencing miR-140-5p expression on the apoptotic rate of (G) H460 and (H) PC-9 cells. The effect of overexpressing or silencing miR-140-5p expression on apoptosis-related proteins of (I) H460 and (J) PC-9 cells. All experiments were performed in triplicate and data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. **P<0.01 vs. NHBE cells, Ctrl mimic or Ctrl inhibitor. miR, microRNA; LUAD, lung adenocarcinoma; LUSC, lung squamous cell carcinoma; NHBE, normal human bronchial epithelial; Ctrl, control.