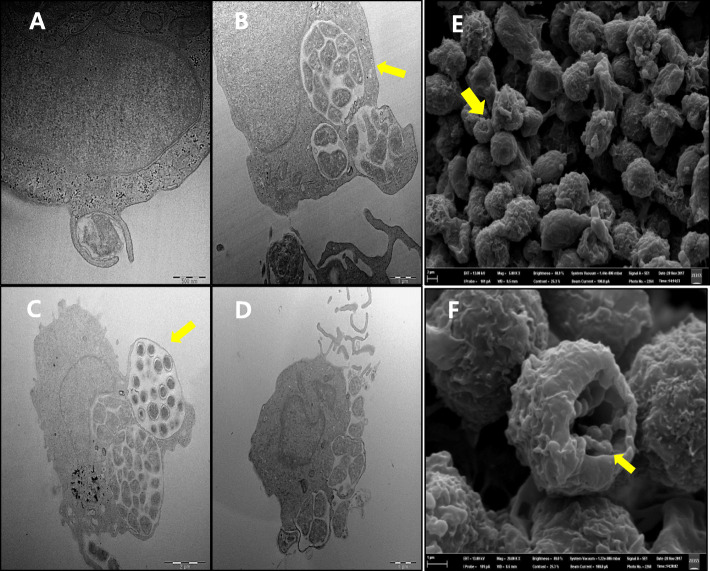
Fig. 4.
Transmission electron microscopy showing the infection stages of isolated A. phagocytophilum KZ_A3-infected HL-60 cells. Adhesion, replication, invasion, and release stages of the isolated A. phagocytophilum within HL-60 cells (a-d). Representative images of dense-cored cells and reticulate cells; the large arrow indicates a dense nucleoid and a ruffled outer membrane, and the spheroid indicates individual dense-cored cells surrounded by a membranous projection (c). Scanning electron micrograph of a cluster of isolated A. phagocytophilum KZ_A3 within HL-60 cells (e, f) A. phagocytophilum KZ_A3 were observed to replicate in a large vesicle inside the cell. Here, the vesicle has ruptured, revealing A. phagocytophilum (c–d, 20000x)