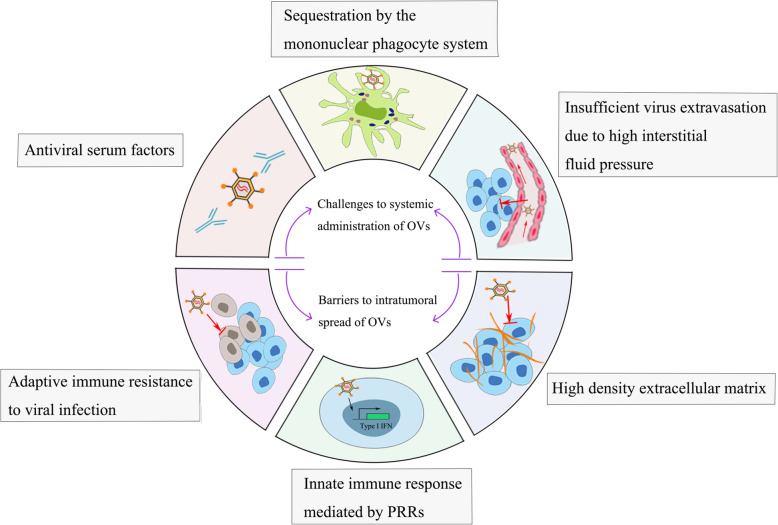
Fig. 1.
Limiting factors affecting the therapeutic effects of oncolytic virotherapy. Viral infection induces the generation of type 1 IFNs by PRR-mediated innate immunity. At the same time, tumor cells may shift sensitivity from the permissive status to a resistant status following durable virotherapy. The dense network of the extracellular matrix also hinders viral spread in tumors. Systemic delivery of naked therapeutic viruses may result in attenuation of viral activity and copies due to phagocytosis by the mononuclear phagocyte system and the neutralizing effects of serum antiviral factors. In addition, there is high interstitial fluid pressure in tumor tissues, which prevents effectively extravasation of the virus from the blood vessel