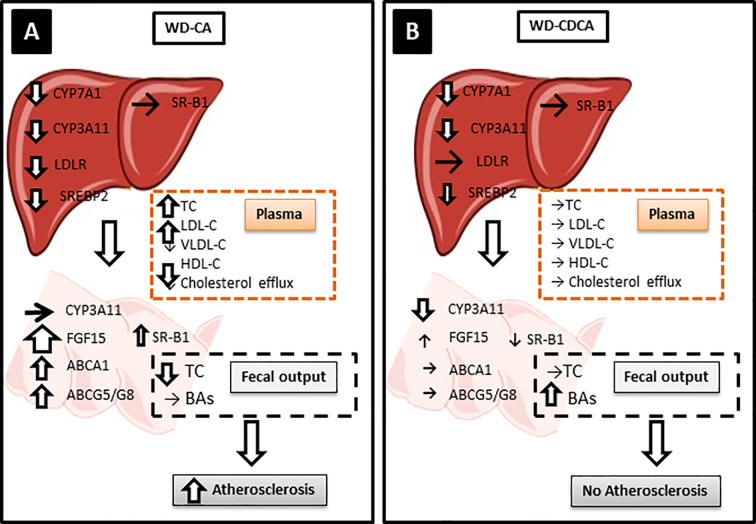
Figure 5.
Possible atherosclerotic mechanisms. Hepatic CYP7A1 and CYP3A11 were downregulated to the same level with both diets but only WD-CA was atherogenic. (A) In WD-CA fed mice, atherosclerosis was mainly driven by high circulating TC concentrations, low HDL-C and high LDL-C, and reduced cholesterol output in feces. The increased plasma LDL-C was attributed to the reduced LDLR leading to a diminished LDL-C uptake by the liver, driven by a decreased SREPB2. In the intestine, WD-CA promoted the release of FGF15 as well as increased expression of ABCA1, ABCG5, ABCG8, and SR-B1. (B) WD-CDCA fed mice failed to develop atherosclerosis, because of low plasma cholesterol, high HDL-C and low LDL-C, the tremendous increase of BAs excretion in feces. In the intestine, WD-CDCA also strongly down regulated CYP3A11, whereas FGF-15 was slightly increased and ABCA1 and ABCG5/G8 were unchanged.