Figure 4.
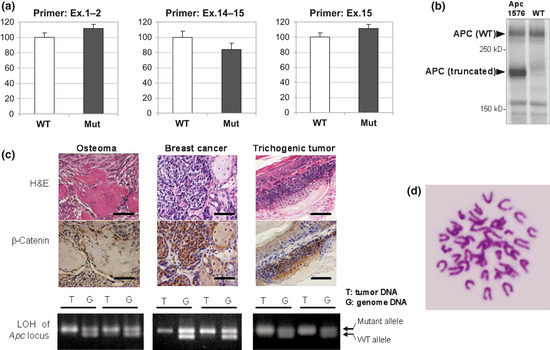
Effects of Apc1576 mutation. (a) Real‐time PCR of Apc mRNA levels in the brains of Apc1576 hetero mutant animals (Mut) or of wild‐type littermates (WT; n = 5 for each genotype). We examined the expression levels using three primer pairs that amplify the region covering exons (Ex.) 1–2 (left), exons 14–15 (center), and exon 15 (right). No significant difference was seen between the hetero mutants and their WT littermates. (b) Immunoblot analysis using an anti‐Apc antibody of protein extracted from the brains of the Apc1576 mutant (left lane) or a WT animal (right lane). In Apc1576 mutants, both truncated product (176 kDa) and WT product (312 kDa) were detected. (c) Nuclear accumulation of β‐catenin and loss of heterozygosity (LOH) of the Apc locus in tumor tissues of Apc1576 mutant animals. As shown in the upper two panels, strong nuclear staining of β‐catenin was detected in all three types of lesions, osteosarcoma (left), breast cancer (center), and trichogenic tumor (right). Bar = 50 μm. In the lower panels, LOH of the Apc gene locus was confirmed in all types of tumors detected in the Apc1576 mutants. Each panel shows the representative results from tumor DNA (T) and genomic DNA (G) of two different mutants in one tumor type. (d) Karyotype analysis of breast cancer cells derived from the Apc1576 mutant. No aneuploidy was observed.
